Page 370 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 370
306 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
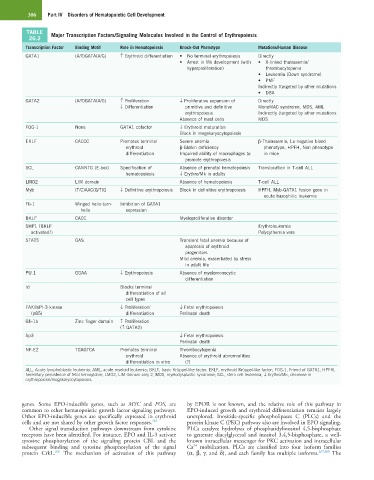
TABLE Major Transcription Factors/Signaling Molecules Involved in the Control of Erythropoiesis
26.2
Transcription Factor Binding Motif Role in Hematopoiesis Knock-Out Phenotype Mutations/Human Disease
GATA1 (A/T)GATA(A/G) ↑ Erythroid differentiation • No terminal erythropoiesis Directly
• Arrest in Mk development (with • X-linked thalassemia/
hyperproliferation) thrombocytopenia
• Leukemia (Down syndrome)
• PMF
Indirectly (targeted by other mutations
• DBA
GATA2 (A/T)GATA(A/G) ↑ Proliferation ↓ Proliferative expansion of Directly
↓ Differentiation primitive and definitive MonoMAC syndrome, MDS, AML
erythropoiesis Indirectly (targeted by other mutations
Absence of mast cells MDS
FOG-1 None GATA1 cofactor ↓ Erythroid maturation
Block in megakaryocytopoiesis
EKLF CACCC Promotes terminal Severe anemia β-Thalassemia, Lu-negative blood
erythroid β-Globin deficiency phenotype, HPFH, Nan phenotype
differentiation Impaired ability of macrophages to in mice
promote erythropoiesis
SCL CANNTG (E-box) Specification of Absence of prenatal hematopoiesis Translocation in T-cell ALL
hematopoiesis ↓ Erythro/Mk in adults
LMO2 LIM domain Absence of hematopoiesis T-cell ALL
Myb (T/C)AAC(G/T)G ↓ Definitive erythropoiesis Block in definitive erythropoiesis HPFH, Myb-GATA1 fusion gene in
acute basophilic leukemia
Fli-1 Winged helix-turn- Inhibition of GATA1
helix expression
BKLF CACC Myeloproliferative disorder
SHP1 (BKLF Erythroleukemia
activated?) Polycythemia vera
STAT5 GAS Transient fetal anemia because of
apoptosis of erythroid
progenitors
Mild anemia, exacerbated by stress
in adult life
PU.1 GGAA ↓ Erythropoiesis Absence of myelomonocytic
differentiation
Id Blocks terminal
differentiation of all
cell types
FAK/IaPI-3 kinase ↓ Proliferation/ ↓ Fetal erythropoiesis
(p85) differentiation Perinatal death
Gfi-1b Zinc finger domain ↑ Proliferation
(↑ GATA2)
Sp3 ↓ Fetal erythropoiesis
Perinatal death
NF-E2 TGAGTCA Promotes terminal Thrombocytopenia
erythroid Absence of erythroid abnormalities
differentiation in vitro (?)
ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; BKLF, basic Krüppel-like factor; EKLF, erythroid Krüppel-like factor; FOG-1, Friend of GATA1; HPFH,
hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin; LMO2, LIM domain only 2; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; SCL, stem cell leukemia; ↓ Erythro/Mk, decrease in
erythropoiesis/megakaryocytopoiesis.
genes. Some EPO-inducible genes, such as MYC and FOS, are by EPOR is not known, and the relative role of this pathway in
common to other hematopoietic growth factor signaling pathways. EPO-induced growth and erythroid differentiation remains largely
Other EPO-inducible genes are specifically expressed in erythroid unexplored. Inositide-specific phospholipases C (PLCs) and the
cells and are not shared by other growth factor responses. 265 protein kinase C (PKC) pathway also are involved in EPO signaling.
Other signal transduction pathways downstream from cytokine PLCs catalyze hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
receptors have been identified. For instance, EPO and IL-3 activate to generate diacylglycerol and inositol 3,4,5-bisphosphate, a well-
tyrosine phosphorylation of the signaling protein CBL and the known intracellular messenger for PKC activation and intracellular
2+
subsequent binding and tyrosine phosphorylation of the signal Ca mobilization. PLCs are classified into four isoform families
266
protein CrkL. The mechanism of activation of this pathway (α, β, γ, and δ), and each family has multiple isoforms. 267,268 The