Page 626 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 626
Chapter 39 Megaloblastic Anemias 535
folate receptors on embryonic neural tube and neural crest cells as way to improve overall folate status in women at risk for NTD
well as the critical bursts of proliferative activity and the need for occurrence. By January 1998, fortification of foods (i.e., rice, flour,
folate to support cell proliferation have been discussed earlier. Thus pasta, macaroni, breads, and cake with folic acid at 140 µg/100 g of
it is critical for a woman to have enough folate in her body before food) was part of American law. This level was chosen to ensure that
conception (periconceptionally) to ensure sufficient availability for women of childbearing age would have an increase in folic acid intake
the embryo. Anencephaly and spina bifida, the commonest NTDs, of at least 100 µg a day, which is about 25% of the recommended
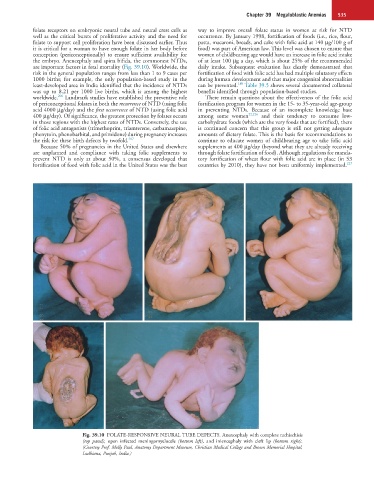
are important factors in fetal mortality (Fig. 39.10). Worldwide, the daily intake. Subsequent evaluation has clearly demonstrated that
risk in the general population ranges from less than 1 to 9 cases per fortification of food with folic acid has had multiple salutatory effects
1000 births; for example, the only population-based study in the during human development and that major congenital abnormalities
189
least-developed area in India identified that the incidence of NTDs can be prevented. Table 39.5 shows several documented collateral
was up to 8.21 per 1000 live births, which is among the highest benefits identified through population-based studies.
206
worldwide. Landmark studies have established the preventive role There remain questions about the effectiveness of the folic acid
of periconceptional folates in both the recurrence of NTD (using folic fortification program for women in the 15- to 35-year-old age-group
acid 4000 µg/day) and the first occurrence of NTD (using folic acid in preventing NTDs. Because of an incomplete knowledge base
400 µg/day). Of significance, the greatest protection by folates occurs among some women 22,226 and their tendency to consume low-
in those regions with the highest rates of NTDs. Conversely, the use carbohydrate foods (which are the very foods that are fortified), there
of folic acid antagonists (trimethoprim, triamterene, carbamazepine, is continued concern that this group is still not getting adequate
phenytoin, phenobarbital, and primidone) during pregnancy increases amounts of dietary folate. This is the basis for recommendations to
the risk for these birth defects by twofold. 207 continue to educate women of childbearing age to take folic acid
Because 50% of pregnancies in the United States and elsewhere supplements at 400 µg/day (beyond what they are already receiving
are unplanned and compliance with taking folic supplements to through folate fortification of food). Although regulations for manda-
prevent NTD is only at about 50%, a consensus developed that tory fortification of wheat flour with folic acid are in place (in 53
227
fortification of food with folic acid in the United States was the best countries by 2010), they have not been uniformly implemented.
Fig. 39.10 FOLATE-RESPONSIVE NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS. Anencephaly with complete rachischisis
(top panel), open infected meningomyelocele (bottom left), and iniencephaly with cleft lip (bottom right).
(Courtesy Prof. Molly Paul, Anatomy Department Museum, Christian Medical College and Brown Memorial Hospital,
Ludhiana, Punjab, India.)