Page 2080 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2080
2054 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 120: Hereditary Qualitative Platelet Disorders 2055
A B
C D
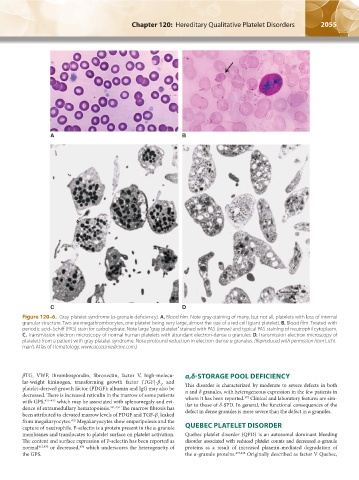
Figure 120–6. Gray platelet syndrome (α-granule deficiency). A. Blood film. Note gray-staining of many, but not all, platelets with loss of internal
granular structure. Two are megathrombocytes, one platelet being very large, almost the size of a red cell (giant platelet). B. Blood film. Treated with
periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain for carbohydrate. Note large “gray platelet” stained with PAS (arrow) and typical PAS staining of neutrophil cytoplasm.
C. Transmission electron microscopy of normal human platelets with abundant electron-dense α granules. D. Transmission electron microscopy of
platelets from a patient with gray platelet syndrome. Note profound reduction in electron-dense α granules. (Reproduced with permission from Licht-
man’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
βTG, VWF, thrombospondin, fibronectin, factor V, high-molecu- α,δ-STORAGE POOL DEFICIENCY
lar-weight kininogen, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β , and
1
platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); albumin and IgG may also be This disorder is characterized by moderate to severe defects in both
decreased. There is increased reticulin in the marrow of some patients α and δ granules, with heterogeneous expression in the few patients in
372
with GPS, 431–433 which may be associated with splenomegaly and evi- whom it has been reported. Clinical and laboratory features are sim-
dence of extramedullary hematopoiesis. 431,434 The marrow fibrosis has ilar to those of δ-SPD. In general, the functional consequences of the
been attributed to elevated marrow levels of PDGF and TGF-β leaked defect in dense granules is more severe than the defect in α granules.
1
from megakaryocytes. Megakaryocytes show emperipolesis and the
412
capture of neutrophils. P-selectin is a protein present in the α-granule QUEBEC PLATELET DISORDER
membranes and translocates to platelet surface on platelet activation. Quebec platelet disorder (QPD) is an autosomal dominant bleeding
The content and surface expression of P-selectin has been reported as disorder associated with reduced platelet counts and decreased α-granule
normal 412,435 or decreased, which underscores the heterogeneity of proteins as a result of increased plasmin-mediated degradation of
436
the GPS. the α-granule proteins. 437,438 Originally described as factor V Quebec,
Kaushansky_chapter 120_p2039-2072.indd 2055 9/21/15 2:20 PM