Page 2078 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2078
2052 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 120: Hereditary Qualitative Platelet Disorders 2053
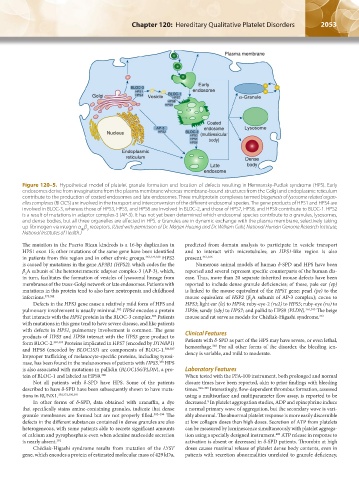
Figure 120–5. Hypothetical model of platelet granule formation and location of defects resulting in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS). Early
endosomes derive from invaginations from the plasma membrane whereas membrane-bound structures from the Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum
contribute to the production of coated endosomes and late endosomes. Three multiprotein complexes termed biogenesis of lysosome related organ-
elles complexes (BLOCS) are involved in the transport and interconversion of the different endosomal species. The gene products of HPS1 and HPS4 are
involved in BLOC-3, whereas those of HPS3, HPS5, and HPS6 are involved in BLOC-2, and those of HPS7, HPS8, and HPS9 contribute to BLOC-1. HPS2
is a result of mutations in adaptor complex-3 (AP-3). It has not yet been determined which endosomal species contribute to α granules, lysosomes,
and dense bodies, but all three organelles are affected in HPS. α Granules are in dynamic exchange with the plasma membrane, selectively taking
up fibrinogen via integrin α β receptors. (Used with permission of Dr. Marjan Huizing and Dr. William Gahl, National Human Genome Research Institute,
IIb 3
National Institutes of Health.)
The mutation in the Puerto Rican kindreds is a 16-bp duplication in predicted from domain analysis to participate in vesicle transport
HPS1 exon 15; other mutations of the same gene have been identified and to interact with microtubules; an HPS1-like region is also
in patients from this region and in other ethnic groups. 363,379,380 HPS2 present. 361,366
is caused by mutations in the gene AP3B1 (HPS2), which codes for the Numerous animal models of human δ-SPD and HPS have been
β A subunit of the heterotetrameric adaptor complex-3 (AP-3), which, reported and several represent specific counterparts of the human dis-
3
in turn, facilitates the formation of vesicles of lysosomal lineage from ease. Thus, more than 20 separate inherited mouse defects have been
membranes of the trans-Golgi network or late endosomes. Patients with reported to include dense granule deficiencies; of these, pale ear (ep)
mutations in this protein tend to also have neutropenia and childhood is linked to the mouse equivalent of the HPS1 gene; pearl (pe) to the
infections. 373,381 mouse equivalent of HSP2 (β A subunit of AP-3 complex); cocoa to
3
Defects in the HPS3 gene cause a relatively mild form of HPS and HPS3; light ear (le) to HPS4; ruby-eye-2 (ru2) to HPS5; ruby-eye (ru) to
pulmonary involvement is usually minimal. HPS4 encodes a protein HPS6; sandy (sdy) to HPS7; and pallid to HPS9 (PLDN). 361,395 The beige
382
that interacts with the HPS1 protein in the BLOC-3 complex. Patients mouse and rat serve as models for Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. 361
383
with mutations in this gene tend to have severe disease, and like patients
with defects in HPS1, pulmonary involvement is common. The gene
products of HPS5 and HPS6 interact with the HPS3 gene product to Clinical Features
form BLOC-2. 384,385 Proteins implicated in HPS7 (encoded by DTNBP1) Patients with δ-SPD as part of the HPS may have severe, or even lethal,
363
and HPS8 (encoded by BLOC1S3) are components of BLOC-1. 386,387 hemorrhage. For all other forms of the disorder, the bleeding ten-
Improper trafficking of melanocyte-specific proteins, including tyrosi- dency is variable, and mild to moderate.
nase, has been found in the melanosomes of patients with HPS5. HPS
388
is also associated with mutations in pallidin (BLOC1S6/PLDN), a pro- Laboratory Features
tein of BLOC-1 and labeled as HPS9. 389 When tested with the PFA-100 instrument, both prolonged and normal
Not all patients with δ-SPD have HPS. Some of the patients closure times have been reported, akin to prior findings with bleeding
described to have δ-SPD have been subsequently shown to have muta- times. 396–399 Interestingly, flow-dependent thrombus formation, assessed
tions in RUNX1. 358,372,390,391 using a multisurface and multiparameter flow assay, is reported to be
In other forms of δ-SPD, data obtained with uranaffin, a dye decreased. In platelet aggregation studies, ADP and epinephrine induce
8
that specifically stains amine-containing granules, indicate that dense a normal primary wave of aggregation, but the secondary wave is vari-
granule membranes are formed but are not properly filled. 392–394 The ably abnormal. The abnormal platelet response is more easily discernible
defects in the different substances contained in dense granules are also at low collagen doses than high doses. Secretion of ATP from platelets
heterogeneous, with some patients able to secrete significant amounts can be measured by luminescence simultaneously with platelet aggrega-
of calcium and pyrophosphate even when adenine nucleotide secretion tion using a specially designed instrument. ATP release in response to
400
is nearly absent. 392 activation is absent or decreased in δ-SPD patients. Thrombin at high
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome results from mutation of the LYST doses causes maximal release of platelet dense body contents, even in
gene, which encodes a protein of estimated molecular mass of 429 kDa, patients with secretion abnormalities unrelated to granule deficiency,
Kaushansky_chapter 120_p2039-2072.indd 2053 9/21/15 2:20 PM