Page 1243 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1243
CHaPTEr 89 Biological Modifiers of Inflammatory Diseases 1205
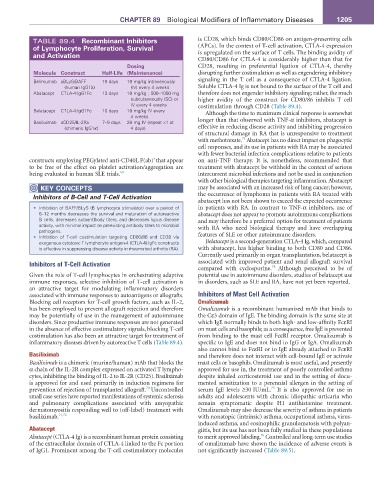
TABLE 89.4 recombinant Inhibitors is CD28, which binds CD80/CD86 on antigen-presenting cells
of Lymphocyte Proliferation, Survival (APCs). In the context of T-cell activation, CTLA-4 expression
and activation is upregulated on the surface of T cells. The binding avidity of
CD80/CD86 for CTLA-4 is considerably higher than that for
Dosing CD28, resulting in preferential ligation of CTLA-4, thereby
Molecule Construct Half-Life (Maintenance) disrupting further costimulation as well as engendering inhibitory
Belimumab aBLyS/BAFF 19 days 10 mg/kg intravenously signaling in the T cell as a consequence of CTLA-4 ligation.
(human IgG1λ) (IV) every 4 weeks Soluble CTLA-4 Ig is not bound to the surface of the T cell and
Abatacept CTLA-4:IgG1Fc 13 days 10 mg/kg ; 500–1000 mg therefore does not engender inhibitory signaling; rather, the much
subcutaneously (SC) or higher avidity of the construct for CD80/86 inhibits T cell
IV every 4 weeks costimulation through CD28 (Table 89.4).
Belatacept CTLA-4:IgG1Fc 10 days 10 mg/kg IV every Although the time to maximum clinical response is somewhat
4 weeks
Basiliximab aCD25/IL-2Ra 7–9 days 20 mg IV (repeat ×1 at longer than that observed with TNF-α inhibitors, abatacept is
(chimeric IgG1κ) 4 days) effective in reducing disease activity and inhibiting progression
of structural damage in RA that is unresponsive to treatment
73
with methotrexate. Abatacept has no direct impact on phagocytic
cell responses, and its use in patients with RA may be associated
with fewer bacterial infection complications relative to patients
constructs employing PEGylated anti-CD40L F(ab)’ that appear on anti-TNF therapy. It is, nonetheless, recommended that
to be free of the effect on platelet activation/aggregation are treatment with abatacept be withheld in the context of serious
being evaluated in human SLE trials. 69 intercurrent microbial infections and not be used in conjunction
with other biological therapies targeting inflammation. Abatacept
KEY CONCEPTS may be associated with an increased risk of lung cancer; however,
Inhibitors of B-Cell and T-Cell Activation the occurrence of lymphoma in patients with RA treated with
abatacept has not been shown to exceed the expected occurrence
• Inhibition of BAFF/BLyS (B lymphocyte stimulator) over a period of in patients with RA. In contrast to TNF-α inhibitors, use of
6–12 months decreases the survival and maturation of autoreactive abatacept does not appear to promote autoimmune complications
B cells, decreases autoantibody titers, and decreases lupus disease and may therefore be a preferred option for treatment of patients
activity, with minimal impact on preexisting antibody titers to microbial with RA who need biological therapy and have overlapping
pathogens.
• Inhibition of T-cell costimulation targeting CD80/86 and CD28 via features of SLE or other autoimmune disorders.
exogenous cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4):IgFc constructs Belatacept is a second-generation CTLA-4 Ig, which, compared
is effective in suppressing disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). with abatacept, has higher binding to both CD80 and CD86.
Currently used primarily in organ transplantation, belatacept is
Inhibitors of T-Cell Activation associated with improved patient and renal allograft survival
74
compared with cyclosporine. Although perceived to be of
Given the role of T-cell lymphocytes in orchestrating adaptive potential use in autoimmune disorders, studies of belatacept use
immune responses, selective inhibition of T-cell activation is in disorders, such as SLE and RA, have not yet been reported.
an attractive target for modulating inflammatory disorders
associated with immune responses to autoantigens or allografts. Inhibitors of Mast Cell Activation
Blocking cell receptors for T-cell growth factors, such as IL-2, Omalizumab
has been employed to prevent allograft rejection and therefore Omalizumab is a recombinant humanized mAb that binds to
may be potentially of use in the management of autoimmune the Cε3 domain of IgE. The binding domain is the same site at
disorders. Since productive immune responses are not generated which IgE normally binds to both high- and low-affinity FcεRI
in the absence of effective costimulatory signals, blocking T-cell on mast cells and basophils; as a consequence, free IgE is prevented
costimulation has also been an attractive target for treatment of from binding to the mast cell FcεRI receptor. Omalizumab is
inflammatory diseases driven by autoreactive T cells (Table 89.4). specific to IgE and does not bind to IgG or IgA. Omalizumab
also cannot bind to FcεRI or to IgE already attached to FcεRI
Basiliximab and therefore does not interact with cell-bound IgE or activate
Basiliximab is a chimeric (murine/human) mAb that blocks the mast cells or basophils. Omalizumab is most useful, and presently
α chain of the IL-2R complex expressed on activated T lympho- approved for use in, the treatment of poorly controlled asthma
cytes, inhibiting the binding of IL-2 to IL-2R (CD25). Basiliximab despite inhaled corticosteroid use and in the setting of docu-
is approved for and used primarily in induction regimens for mented sensitization to a perennial allergen in the setting of
75
70
prevention of rejection of transplanted allograft. Uncontrolled serum IgE levels ≥30 IU/mL. It is also approved for use in
small case series have reported manifestations of systemic sclerosis adults and adolescents with chronic idiopathic urticaria who
and pulmonary complications associated with amyopathic remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment.
dermatomyositis responding well to (off-label) treatment with Omalizumab may also decrease the severity of asthma in patients
basiliximab. 71,72 with nonatopic (intrinsic) asthma, occupational asthma, virus-
induced asthma, and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyan-
Abatacept giitis, but its use has not been fully studied in these populations
76
Abatacept (CTLA-4 Ig) is a recombinant human protein consisting to merit approved labeling. Controlled and long-term use studies
of the extracellular domain of CTLA-4 linked to the Fc portion of omalizumab have shown the incidence of adverse events is
of IgG1. Prominent among the T-cell costimulatory molecules not significantly increased (Table 89.5).