Page 1244 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1244
1206 ParT TEN Prevention and Therapy of Immunological Diseases
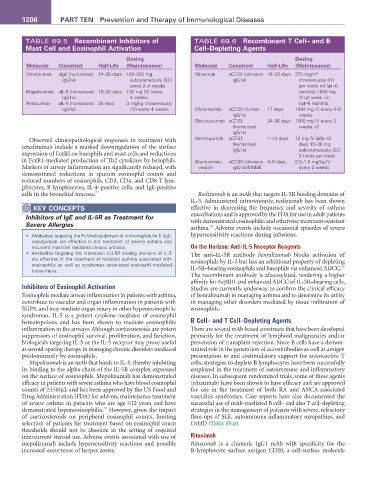
TABLE 89.5 recombinant Inhibitors of TABLE 89.6 recombinant T Cell– and B
Mast Cell and Eosinophil activation Cell–Depleting agents
Dosing Dosing
Molecule Construct Half-Life (Maintenance) Molecule Construct Half-Life (Maintenance)
Omalizumab aIgE (humanized 24–26 days 150–300 mg Rituximab aCD20 (chimeric 18–23 days 375 mg/m 2
IgG1κ) subcutaneously (SC) IgG1κ) intravenously (IV)
every 2–4 weeks per week ×4 (q4–6
Mepolizumab aIL-5 (humanized 16–22 days 100 mg SC every months) 1000 mg
IgG1κ) 4 weeks IV q2 week ×2
Reslizumab aIL-5 (humanized 24 days 3 mg/kg intravenously (q4–6 months)
IgG4κ) (IV) every 4 weeks Ofatumumab aCD20 (human 17 days 1000 mg IV every 4–8
IgG1κ) weeks
Obinutuzumab aCD20 24–36 days 1000 mg IV every 2
(humanized weeks ×2
IgG1κ)
Observed clinicopathological responses to treatment with Alemtuzumab aCD52 1–14 days 12 mg IV daily ×5
omalizumab include a marked downregulation of the surface (humanized days 10–30 mg
IgG1κ)
subcutaneously (SC)
expression of FcεRI on basophils and mast cells and reductions 3 times per week
in FcεR1-mediated production of Th2 cytokines by basophils. Brentuximab- aCD30 (chimeric 4–6 days 0.3–1.8 mg/kg IV
Markers of airway inflammation are significantly reduced, with vedotin IgG1κ):MMAE every 3 weeks
demonstrated reductions in sputum eosinophil counts and
reduced numbers of eosinophils, CD3, CD4, and CD8 T lym-
phocytes, B lymphocytes, IL-4–positive cells, and IgE-positive
cells in the bronchial mucosa. 77 Reslizumab is an mAb that targets IL-5R binding domains of
IL-5. Administered intravenously, reslizumab has been shown
KEY CONCEPTS effective in decreasing the frequency and severity of asthma
Inhibitors of IgE and IL-5R as Treatment for exacerbations and is approved by the FDA for use in adult patients
Severe Allergies with demonstrated eosinophilia and otherwise treatment-resistant
79
asthma. Adverse events include occasional episodes of severe
• Antibodies targeting the Fc binding domain of immunoglobulin E (IgE; hypersensitivity reactions during infusions.
omalizumab) are effective in the treatment of severe asthma and
recurrent mast-cell mediated chronic urticaria. On the Horizon: Anti-IL-5 Receptor Reagents
• Antibodies targeting the interleukin (IL)-5R binding domains of IL-5 The anti–IL-5R antibody benralizumab blocks activation of
are effective in the treatment of resistant asthma associated with eosinophils by IL-5 but has an additional property of depleting
eosinophilia as well as syndromes associated eosinophil-mediated 80
tissue injury. IL-5R–bearing eosinophils and basophils via enhanced ADCC.
The recombinant antibody is afucosylated, rendering a higher
affinity for FcγRIII and enhanced ADCC of IL-5R–bearing cells.
Inhibitors of Eosinophil Activation Studies are currently underway to confirm the clinical efficacy
Eosinophils mediate airway inflammation in patients with asthma, of benralizumab in managing asthma and to determine its utility
contribute to vascular and organ inflammation in patients with in managing other disorders mediated by tissue infiltration of
EGPA, and may mediate organ injury in other hypereosinophilic eosinophils.
syndromes. IL-5 is a potent cytokine mediator of eosinophil
hematopoiesis and has been shown to mediate eosinophilic B Cell– and T Cell–Depleting Agents
inflammation in the airways. Although corticosteroids are potent There are several mAb-based constructs that have been developed
suppressors of eosinophil survival, proliferation, and function, primarily for the treatment of lymphoid malignancies and/or
biologicals targeting IL-5 or the IL-5 receptor may prove useful prevention of transplant rejection. Since B cells have a demon-
as steroid-sparing therapy in managing chronic disorders mediated strated role in the generation of autoantibodies as well as antigen
predominantly by eosinophils. presentation to and costimulatory support for autoreactive T
Mepolizumab is an mAb that binds to IL-5, thereby inhibiting cells, strategies to deplete B lymphocytes have been successfully
its binding to the alpha chain of the IL-5R complex expressed employed in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory
on the surface of eosinophils. Mepolizumab has demonstrated diseases. In subsequent randomized trials, some of these agents
efficacy in patients with severe asthma who have blood eosinophil (rituximab) have been shown to have efficacy and are approved
counts of ≥150/µL and has been approved by the US Food and for use in the treatment of both RA and ANCA-associated
Drug Administration (FDA) for add-on, maintenance treatment vasculitis syndromes. Case reports have also documented the
of severe asthma in patients who are age ≥12 years and have successful use of mAb-mediated B cell– and also T cell–depleting
78
demonstrated hypereosinophilia. However, given the impact strategies in the management of patients with severe, refractory
of corticosteroids on peripheral eosinophil counts, limiting flare-ups of SLE, autoimmune inflammatory myopathies, and
selection of patients for treatment based on eosinophil count GvHD (Table 89.6).
thresholds should not be absolute in the setting of required
intercurrent steroid use. Adverse events associated with use of Rituximab
mepolizumab include hypersensitivity reactions and possible Rituximab is a chimeric IgG1 mAb with specificity for the
increased occurrence of herpes zoster. B-lymphocyte surface antigen CD20, a cell-surface molecule