Page 459 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 459
CHAPTER 22 ■ Lymphoid and Plasma Cell Neoplasms 443
Lymphomas ■ Ho gkin ly pho is ch r cterize by the presence o
Ree -Sternberg cells.
■ Ly pho s re closely rel te to leuke i s. Initi lly, ly -
pho s re conf ne to the ly ph no es, but they y Plasma Cell Dyscrasias
spillover into the bloo in the leuke ic ph se.
■ Te REAL n WHO cl ssif c tions inclu e Ho gkin ■ Multiple yelo is lign nt pl s cell ise se, typi-
ise se n NHL. T e presence or bsence o Ree - c lly o the bone rrow.
Sternberg cells is critic l in est blishing i gnosis ■ Pl s cell leuke i is consi ere to be or o ul-
Ho gkin. tiple yelo , not sep r te entity; however, incre se
■ Leuke ic ph se o NHLs c n be seen in s ll B-cell ly - nu bers o pl s cells re oun in the peripher l bloo
pho s such s “in situ” ollicul r ly pho th t h s r ther th n in the bone rrow.
been ren e “in situ” ollicul r neopl si (ISFN), MCL, ■ Te outst n ing l bor tory ch r cteristics inclu e the
rgin l zone B-cell ly pho n ly phopl s cytic presence o Bence-Jones protein in the urine n n
ly pho (LPL). bnor l seru n /or urin ry electrophoretic p ttern.
■ Other NHL ly pho s inclu e i use LBCL, not other- ■ Pl s cell isor ers rel te to MM re s ol ering MM,
wise specif e (DLBCL, NOS). In ition, EBV+ LBCLs IgM onoclon l g op thy o un eter ine signif -
o the el erly is now c lle EBV+ DLBCL < NOS). c nce (IgM-MGUS), non-IgM onoclon l g op thy
■ Burkitt’s ly pho in the WHO cl ssif c tion co bines o un eter ine signif c nce (Non-IgM-MGUS), light
the cute ly phobl stic leuke i (ALL-3 o the FAB ch in onoclon l g op thy o un eter ine signif -
cl ssif c tion) with Burkitt’s ly pho . Most but not ll c nce, solit ry pl s cyto , n solit ry pl s cyto
ALL-L3 c ses ppe r to be the leuke ic ph se o Burkitt’s with ini l rrow involve ent.
ly pho . High-gr e ly pho s less co only h ve ■ WM is lign nt ly phocyte–pl s cell proli er tive
leuke ic ph se. isor er with bnor lly l rge ounts o the g
■ Tree types o Burkitt’s ly pho (BL), high-gr e globulin type (19S or IgM).
NHL ly pho , re recognize : A ric n (en e ic), spo- ■ Abnor l seru electrophoresis p tterns n the pres-
r ic, n i uno ef ciency ssoci te . ence o cryoglobulin re ch r cteristic.
CASE STUDIES
Case Study 22.1
A 58-ye r-ol e le e ic l recor s libr ri n w s it-
te to the hospit l or inor elective surgery. Although the
p tient h been co pl ining o gener l l ise n tigue,
she suspecte th t it w s work-rel te proble r ther th n
physic l proble . Physic l ex in tion reve le th t she
h both cervic l n supr cl vicul r ly ph enop thy.
■ Laboratory Data
Her preoper tive bloo count reve le th t her erythrocytes
n he oglobin were within nor l r nges; however, her
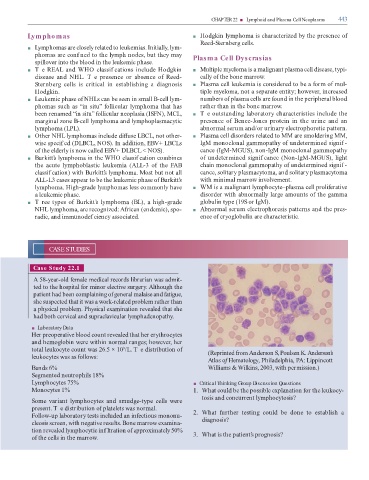
tot l leukocyte count w s 26.5 × 10 /L. T e istribution o (Reprinte ro An erson S, Poulsen K. Anderson’s
9
leukocytes w s s ollows:
Atlas o Hematology, Phil elphi , PA: Lippincott
B n s 6% Willi s & Wilkins, 2003, with per ission.)
Seg ente neutrophils 18%
Ly phocytes 75% ■ Critical Thinking Group Discussion Questions
Monocytes 1% 1. Wh t coul be the possible expl n tion or the leukocy-
tosis n concurrent ly phocytosis?
So e v ri nt ly phocytes n s u ge-type cells were
present. T e istribution o pl telets w s nor l.
Follow-up l bor tory tests inclu e n in ectious ononu- 2. Wh t urther testing coul be one to est blish
cleosis screen, with neg tive results. Bone rrow ex in - i gnosis?
tion reve le ly phocytic inf ltr tion o pproxi tely 50%
o the cells in the rrow. 3. Wh t is the p tient’s prognosis?