Page 579 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 579
CHAPTER 28 ■ Disorders of Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Blood Coagulation Factors, Hypercoagulable State, and Anticoagulant Therapy 563
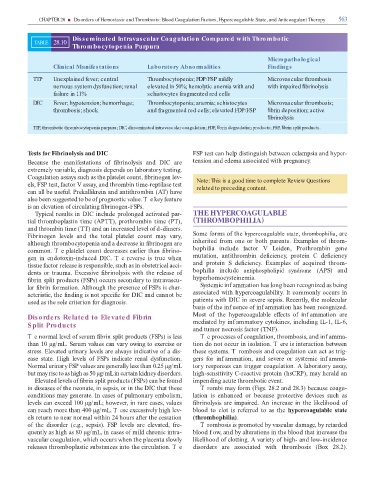
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Compared w ith Thrombotic
TABLE 28.10
Thrombocytopenia Purpura
Micropathological
Clinical Manifestations Laboratory Abnormalities Findings
TTP Unexplained fever; central Thrombocytopenia; FDP/FSP mildly Microvascular thrombosis
nervous system dysfunction; renal elevated in 50%; hemolytic anemia with and with impaired brinolysis
failure in 11% schistocytes fragmented red cells
DIC Fever; hypotension; hemorrhage; Thrombocytopenia; anemia; schistocytes Microvascular thrombosis;
thrombosis; shock and fragmented red cells; elevated FDP/FSP brin deposition; active
brinolysis
TTP, thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; FDP, brin degradation products; FSP, brin split products.
ests or Fibrinolysis and DIC FSP test can he istinguish between ec a sia an hy er-
Because the ani estations o brino ysis an DIC are tension an e e a associate with regnancy.
extre e y variab e, iagnosis e en s on aboratory testing.
Coagu ation assays such as the ate et count, brinogen ev- Note: This is a good time to complete Review Questions
e s, FSP test, actor V assay, an thro bin ti e-re ti ase test related to preceding content.
can a be use u . Preka ikrein an antithro bin (A ) have
a so been suggeste to be o rognostic va ue. T e key eature
is an e evation o circu ating brinogen-FSPs.
y ica resu ts in DIC inc u e ro onge activate ar- HE HYPERCOAGULABLE
tia thro bo astin ti e (AP ), rothro bin ti e (P ), HROMBOPHILIA
an thro bin ti e ( ) an an increase eve o d- i ers.
Fibrinogen eve s an the tota ate et count ay vary, So e or s o the hypercoagulable state, thrombophilia, are
a though thro bocyto enia an a ecrease in brinogen are inherite ro one or both arents. Exa es o thro -
co on. T e ate et count ecreases ear ier than brino- bo hi ia inc u e actor V Lei en, Prothro bin gene
gen in en otoxin-in uce DIC. T e reverse is true when utation, antithro bin e ciency, rotein C e ciency
tissue actor re ease is res onsib e, such as in obstetrica acci- an rotein S e ciency. Exa es o acquire thro -
ents or trau a. Excessive brino ysis with the re ease o bo hi ia inc u e antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) an
brin s it ro ucts (FSPs) occurs secon ary to intravascu- hy erho ocysteine ia.
ar brin or ation. A though the resence o FSPs is char- Syste ic inf a ation has ong been recognize as being
acteristic, the n ing is not s eci c or DIC an cannot be associate with hy ercoagu abi ity. It co on y occurs in
use as the so e criterion or iagnosis. atients with DIC in severe se sis. Recent y, the o ecu ar
basis o the inf uence o inf a ation has been recognize .
Disorders Related to Elevated Fibrin Most o the hy ercoagu ab e e ects o inf a ation are
Split Products e iate by inf a atory cytokines, inc u ing IL-1, IL-6,
an tu or necrosis actor ( NF).
Te nor a eve o seru brin s it ro ucts (FSPs) is ess T e rocesses o coagu ation, thro bosis, an inf a a-
than 10 µg/ L. Seru va ues can vary owing to exercise or tion o not occur in iso ation. T ere is interaction between
stress. E evate urinary eve s are a ways in icative o a is- these syste s. T ro bosis an coagu ation can act as trig-
ease state. High eve s o FSPs in icate rena ys unction. gers or inf a ation, an severe or syste ic inf a a-
Nor a urinary FSP va ues are genera y ess than 0.25 µg/ L tory res onses can trigger coagu ation. A aboratory assay,
but ay rise to as high as 50 µg/ L in certain ki ney isor ers. high-sensitivity C-reactive rotein (hsCRP), ay hera an
E evate eve s o brin s it ro ucts (FSPs) can be oun i en ing acute thro botic event.
in iseases o the neonate, in se sis, or in the DIC that these T ro bi ay or (Figs. 28.2 an 28.3) because coagu-
con itions ay generate. In cases o u onary e bo is , ation is enhance or because rotective evices such as
eve s can excee 100 µg/ L; however, in rare cases, va ues brino ysis are i aire . An increase in the ike ihoo o
can reach ore than 400 µg/ L. T ese excessive y high ev- b oo to c ot is re erre to as the hypercoagulable state
e s return to near nor a within 24 hours a er the cessation (thrombophilia).
o the isor er (e.g., se sis). FSP eve s are e evate , re- T ro bosis is ro ote by vascu ar a age, by retar e
quent y as high as 80 µg/ L, in cases o i chronic intra- b oo f ow, an by a terations in the b oo that increase the
vascu ar coagu ation, which occurs when the acenta s ow y ike ihoo o c otting. A variety o high- an ow- inci ence
re eases thro bo astic substances into the circu ation. T e isor ers are associate with thro bosis (Box 28.2).