Page 454 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 454
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 52 Blood & Tissue Protozoa
443
C
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com E mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
B
A
D
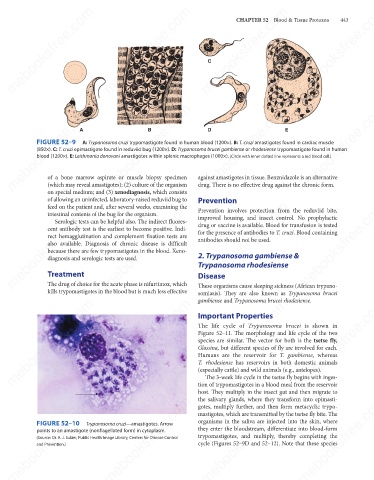
FIGURE 52–9
A: Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote found in human blood (1200×). B: T. cruzi amastigotes found in cardiac muscle
(850×). C: T. cruzi epimastigote found in reduviid bug (1200×). D: Trypanosoma brucei gambiense or rhodesiense trypomastigote found in human
blood (1200×). E: Leishmania donovani amastigotes within splenic macrophages (1000×). (Circle with inner dotted line represents a red blood cell.)
of a bone marrow aspirate or muscle biopsy specimen
drug. There is no effective drug against the chronic form.
(which may reveal amastigotes); (2) culture of the organism
on special medium; and (3) xenodiagnosis, which consists
Prevention
of allowing an uninfected, laboratory-raised reduviid bug to against amastigotes in tissue. Benznidazole is an alternative
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com drug or vaccine is available. Blood for transfusion is tested mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
feed on the patient and, after several weeks, examining the
Prevention involves protection from the reduviid bite,
intestinal contents of the bug for the organism.
improved housing, and insect control. No prophylactic
Serologic tests can be helpful also. The indirect fluores-
cent antibody test is the earliest to become positive. Indi-
for the presence of antibodies to T. cruzi. Blood containing
rect hemagglutination and complement fixation tests are
antibodies should not be used.
also available. Diagnosis of chronic disease is difficult
because there are few trypomastigotes in the blood. Xeno-
2. Trypanosoma gambiense &
diagnosis and serologic tests are used.
Trypanosoma rhodesiense
Treatment
The drug of choice for the acute phase is nifurtimox, which
These organisms cause sleeping sickness (African trypano-
kills trypomastigotes in the blood but is much less effective Disease
somiasis). They are also known as Trypanosoma brucei
gambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com The life cycle of Trypanosoma brucei is shown in mebooksfree.com
Important Properties
Figure 52–11. The morphology and life cycle of the two
species are similar. The vector for both is the tsetse fly,
Glossina, but different species of fly are involved for each.
Humans are the reservoir for T. gambiense, whereas
T. rhodesiense has reservoirs in both domestic animals
(especially cattle) and wild animals (e.g., antelopes).
The 3-week life cycle in the tsetse fly begins with inges-
tion of trypomastigotes in a blood meal from the reservoir
host. They multiply in the insect gut and then migrate to
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Trypanosoma cruzi—amastigotes. Arrow organisms in the saliva are injected into the skin, where mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
the salivary glands, where they transform into epimasti-
gotes, multiply further, and then form metacyclic trypo-
mastigotes, which are transmitted by the tsetse fly bite. The
FIGURE 52–10
they enter the bloodstream, differentiate into blood-form
points to an amastigote (nonflagellated form) in cytoplasm.
trypomastigotes, and multiply, thereby completing the
(Source: Dr. A. J. Sulzer, Public Health Image Library, Centers for Disease Control
cycle (Figures 52–9D and 52–12). Note that these species
and Prevention.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com