Page 25 - Electrostatics 11
P. 25
Grade 11 © GC Shiba
☻ State and explain Gauss law in electrostatics. Use it to find the
electric field intensity due to a line charge.
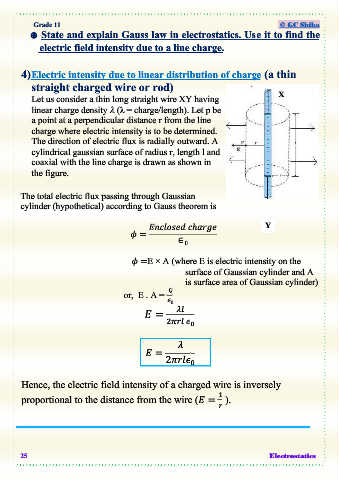
4) Electric intensity due to linear distribution of charge (a thin
straight charged wire or rod)
Let us consider a thin long straight wire XY having X
linear charge density (λ = charge/length). Let p be
a point at a perpendicular distance r from the line
charge where electric intensity is to be determined.
The direction of electric flux is radially outward. A
cylindrical gaussian surface of radius r, length l and
coaxial with the line charge is drawn as shown in
the figure.
The total electric flux passing through Gaussian
cylinder (hypothetical) according to Gauss theorem is
ℎ Y
=
∈ 0
=E × A (where E is electric intensity on the
surface of Gaussian cylinder and A
is surface area of Gaussian cylinder)
or, E . A =
0
=
2 0
=
2 0
Hence, the electric field intensity of a charged wire is inversely
1
proportional to the distance from the wire ( = ).
25 Electrostatics