Page 63 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 63
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
2. There is a phase change in the light that passed through (b) Thin cell wall
different refractive indices. Such phase difference can (c) (i) Cell X is non-living whereas cell Y is living.
be neutralised or darkened by using suitable phase
plate i.e. clear plastic of certain thickness and shape. Cell X with wall thicken evenly while cell Y
with wall thickened at corners.
3. Electron beam has a wavelength shorter than 10 nm. (ii) Cell X provides mechanical support with
The limit of resolution of a microscope is about half
the wavelength of the radiation used to view the lignified wall while cell Z provides support
with non-lignified wall.
2 specimen. Two points shorter than 200 nm is beyond
the resolution of the light microscope and therefore Essay Questions
electron microscope is required to resolve them.
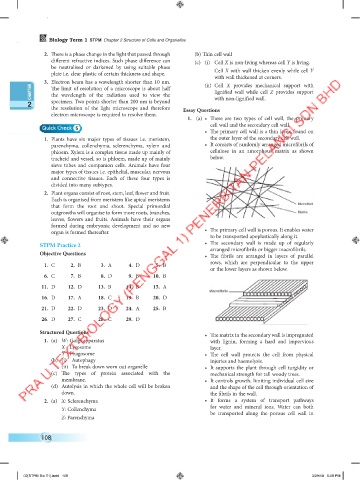
1. (a) • There are two types of cell wall, the primary
cell wall and the secondary cell wall.
5
• The primary cell wall is a thin layer, found on
1. Plants have six major types of tissues i.e. meristem, the outer layer of the secondary cell wall.
parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem and • It consists of randomly arranged microfibrils of
phloem. Xylem is a complex tissue made up mainly of cellulose in an amorphous matrix as shown
tracheid and vessel, so is phloem, made up of mainly below.
sieve tubes and companion cells. Animals have four
major types of tissues i.e. epithelial, muscular, nervous
and connective tissues. Each of these four types is
divided into many subtypes.
2. Plant organs consist of root, stem, leaf, flower and fruit.
Each is organised from meristem like apical meristems
that form the root and shoot. Special primordial Microfibril
outgrowths will organise to form more roots, branches, Matrix
leaves, flowers and fruits. Animals have their organs
formed during embryonic development and no new
organ is formed thereafter. • The primary cell wall is porous. It enables water
to be transported apoplastically along it.
STPM Practice 2 • The secondary wall is made up of regularly
arranged microfibrils or bigger macrofibrils.
Objective Questions • The fibrils are arranged in layers of parallel
rows, which are perpendicular to the upper
1. C 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. B
or the lower layers as shown below.
6. C 7. B 8. D 9. B 10. B
11. D 12. D 13. B 14. B 15. A
Macrofibrils
16. D 17. A 18. C 19. B 20. D
21. D 22. D 23. D 24. A 25. B
26. D 27. C 28. C 29. D
Structured Questions • The matrix in the secondary wall is impregnated
1. (a) W : Golgi apparatus with lignin, forming a hard and impervious
X : Lysosome layer.
Y : Phagosome • The cell wall protects the cell from physical
(b) (i) Autophagy injuries and haemolysis.
(ii) To break down worn out organelle • It supports the plant through cell turgidity or
(c) The types of protein associated with the mechanical strength for tall woody trees.
membrane. • It controls growth, limiting individual cell size
(d) Autolysis in which the whole cell will be broken and the shape of the cell through orientation of
down. the fibrils in the wall.
2. (a) X: Sclerenchyma • It forms a system of transport pathways
Y: Collenchyma for water and mineral ions. Water can both
be transported along the porous cell wall in
Z: Parenchyma
108
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 108 3/29/18 5:08 PM