Page 37 - Pra U STPM 2022 Penggal 2 - Mathematics
P. 37
Mathematics Semester 2 STPM Chapter 4 Differential Equations
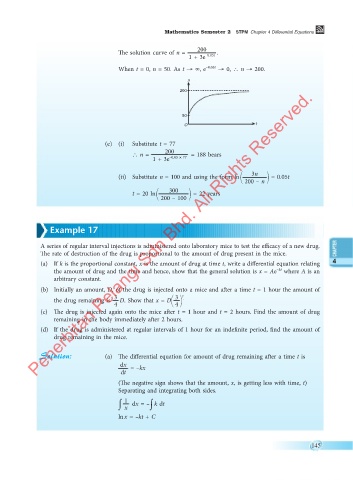
The solution curve of n = 200 .
1 + 3e –0.05t
When t = 0, n = 50. As t → ∞, e –0.05t → 0, \ n → 200.
n
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
200
50
O t
(e) (i) Substitute t = 77
\ n = 200 = 188 bears
1 + 3e –0.05 × 77
3n
(ii) Substitute n = 100 and using the form ln 1 200 – n 2 = 0.05t
300
t = 20 ln 1 200 – 100 2 = 22 years
Example 17
A series of regular interval injections is administered onto laboratory mice to test the efficacy of a new drug.
The rate of destruction of the drug is proportional to the amount of drug present in the mice.
(a) If k is the proportional constant, x is the amount of drug at time t, write a differential equation relating 4
–kt
the amount of drug and the time and hence, show that the general solution is x = Ae where A is an
arbitrary constant.
(b) Initially an amount, D, of the drug is injected onto a mice and after a time t = 1 hour the amount of
3
the drug remaining is 3 D. Show that x = D 1 2 t .
4 4
(c) The drug is injected again onto the mice after t = 1 hour and t = 2 hours. Find the amount of drug
remaining in the body immediately after 2 hours.
(d) If the drug is administered at regular intervals of 1 hour for an indefinite period, find the amount of
drug remaining in the mice.
Solution: (a) The differential equation for amount of drug remaining after a time t is
dx = –kx
dt
(The negative sign shows that the amount, x, is getting less with time, t)
Separating and integrating both sides.
1
∫ dx = – k dt
∫
x
ln = –kt + C
x
145
04 STPM Math(T) T2.indd 145 28/01/2022 5:44 PM