Page 36 - The Effect of Hydrogen and Hydrides - ebook first test
P. 36
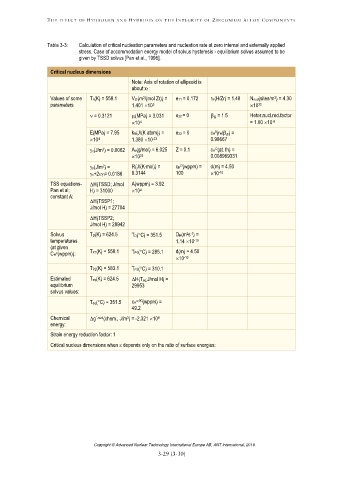
Table 3-3: Calculation of critical nucleation parameters and nucleation rate at zero internal and externally applied
stress. Case of accommodation energy model of solvus hysteresis - equilibrium solvus assumed to be
given by TSSD solvus [Pan et al., 1996].
Critical nucleus dimensions
Note: Axis of rotation of ellipsoid is
about x1:
Values of some Tn(K) = 558.1 VZr(m /(mol Zr)) = e11 = 0.172 rH(H/Zr) = 1.48 Nnud(sites/m ) = 4.30
3
3
parameters 1.401 10 10
5
22
= 0.3121 (MPa) = 3.031 e22 = 0 β = 1.5 Heter.nucl.red.factor
δ
-6
10 = 1.00 10
4
E(MPa) = 7.95 kB(J/(K atom)) = e33 = 0 cH (rH/β ) =
δ
δ
10 1.380 10 0.98667
4
-23
O
c(J/m ) = 0.0062 Ao(g/mol) = 6.025 Z = 0.1 cH (at. fn) =
2
23
10 0.008969331
O
2
p(J/m ) = R(J/(K∙mol)) = cH (wppm) = d(m) = 4.50
-10
c+2i= 0.0186 8.3144 100 10
TSS equations- H(TSSD; J/mol A(wppm) = 3.92
Pan et al; H) = 31000 10
4
constant A:
H(TSSP1;
J/mol H) = 27704
H(TSSP2;
J/mol H) = 28942
Solvus TD(K) = 624.5 TD(C) = 351.5 DH(m s ) =
2 -1
temperatures 1.14 10
-10
(at given
CH (wppm)): TP1(K) = 558.1 TP1(C) = 285.1 d(m) = 4.50
o
10
-10
TP2(K) = 583.1 TP2(C) = 310.1
Estimated Teq(K) = 624.5 H(Teq;J/mol H) =
equilibrium 29953
solvus values:
Teq(C) = 351.5 cH s, eq (wppm) =
49.2
Chemical g , nucl (chem., J/m ) = -2.321 10
8
3
energy:
Strain energy reduction factor: 1
Critical nucleus dimensions when depends only on the ratio of surface energies:
Copyright © Advanced Nuclear Technology International Europe AB, ANT International, 2019.