Page 62 - SP015 Past Years PSPM Chapter 6 -14 Ver 2020
P. 62
PHYSICS PSPM SEM 1 1999 - 2017
PSPM 2015/2016 SF016/2 No. 8(a)(ii)
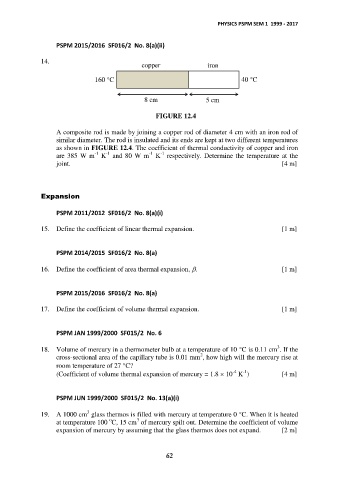
14. copper iron
160 C 40 C
8 cm 5 cm
FIGURE 12.4
A composite rod is made by joining a copper rod of diameter 4 cm with an iron rod of
similar diameter. The rod is insulated and its ends are kept at two different temperatures
as shown in FIGURE 12.4. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of copper and iron
-1
-1
-1
-1
are 385 W m K and 80 W m K respectively. Determine the temperature at the
joint. [4 m]
Expansion
PSPM 2011/2012 SF016/2 No. 8(a)(i)
15. Define the coefficient of linear thermal expansion. [1 m]
PSPM 2014/2015 SF016/2 No. 8(a)
16. Define the coefficient of area thermal expansion, . [1 m]
PSPM 2015/2016 SF016/2 No. 8(a)
17. Define the coefficient of volume thermal expansion. [1 m]
PSPM JAN 1999/2000 SF015/2 No. 6
3
18. Volume of mercury in a thermometer bulb at a temperature of 10 C is 0.11 cm . If the
2
cross-sectional area of the capillary tube is 0.01 mm , how high will the mercury rise at
room temperature of 27 C?
-4
-1
(Coefficient of volume thermal expansion of mercury = 1.8 10 K ) [4 m]
PSPM JUN 1999/2000 SF015/2 No. 13(a)(i)
3
19. A 1000 cm glass thermos is filled with mercury at temperature 0 C. When it is heated
3
o
at temperature 100 C, 15 cm of mercury spilt out. Determine the coefficient of volume
expansion of mercury by assuming that the glass thermos does not expand. [2 m]
62