Page 181 - Health, Population and Environment Education 10
P. 181
Gonorrhoea : At a glance
Speciality : Infectious disease
Causative agent : Neisseria gonorrhoea
Modes of transmission : Unsafe sexual contact with the infected partner
Symptoms : None, burning with urination, vaginal discharge, discharge
from the penis, pelvic pain, testicular pain
Diagnosis : Testing with urine, urethra in males or cervix in females
Prevention : Condoms, having sex with only one partner who is
uninfected, not having sex with infected partner
Treatment : Ceftriaxone by injection and azithromycin by mouth
Gonorrhoea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral,
anal and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth.
Gonorrhoea affects about 0.8% of women and 0.6% of men. An estimated 33 to 106 million
new cases occur each year, out of the 498 million new cases curable STI- which also
includes Syphilis, Chlamydia and Trichomoniasis. Infections in women most commonly
occur when they are young adults.
Gonorrhoea affects both males and females. This disease infects urethra, rectum, eyes,
throat, etc. It produces lesions around urethra. It may also affect epididymis and inner
part of uterus. The person having gonorrhoea has an increased risk of getting infected
with syphilis and other STI’s.
Modes of Transmission
i. Through unsafe sexual intercourse with the infected partner
ii. Contact with the materials used by the patient
iii. Through contaminated blood transfusion
iv. Through contaminated needle, razor, blade, syringe, etc.
v. From infected mother to her unborn child
Major Symptoms
i. Frequent urination
ii. Burning sensation while urinating
iii. Vaginal discharge
iv. Discharge from penis
v. Swelling of urethra and difficulty in urination
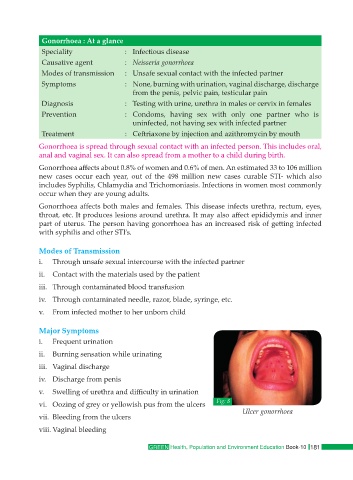
vi. Oozing of grey or yellowish pus from the ulcers Fig: 8
Ulcer gonorrhoea
vii. Bleeding from the ulcers
viii. Vaginal bleeding
GREEN Health, Population and Environment Education Book-10 181