Page 19 - MALAYSIAN PATIENT SAFETY GOALS
P. 19
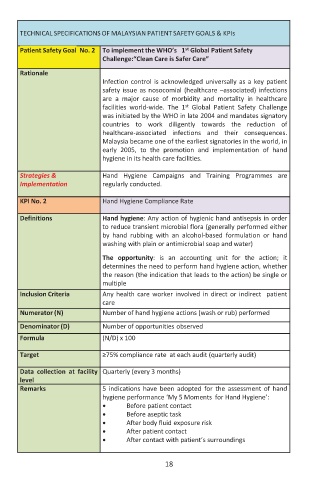
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS OF MALAYSIAN PATIENT SAFETY GOALS & KPIs
st
Patient Safety Goal No. 2 To implement the WHO’s 1 Global Patient Safety
Challenge:“Clean Care is Safer Care”
Rationale
Infection control is acknowledged universally as a key patient
safety issue as nosocomial (healthcare –associated) infections
are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in healthcare
st
facilities world-wide. The 1 Global Patient Safety Challenge
was initiated by the WHO in late 2004 and mandates signatory
countries to work diligently towards the reduction of
healthcare-associated infections and their consequences.
Malaysia became one of the earliest signatories in the world, in
early 2005, to the promotion and implementation of hand
hygiene in its health care facilities.
Strategies & Hand Hygiene Campaigns and Training Programmes are
Implementation regularly conducted.
KPI No. 2 Hand Hygiene Compliance Rate
Definitions Hand hygiene: Any action of hygienic hand antisepsis in order
to reduce transient microbial flora (generally performed either
by hand rubbing with an alcohol-based formulation or hand
washing with plain or antimicrobial soap and water)
The opportunity: is an accounting unit for the action; it
determines the need to perform hand hygiene action, whether
the reason (the indication that leads to the action) be single or
multiple
Inclusion Criteria Any health care worker involved in direct or indirect patient
care
Numerator (N) Number of hand hygiene actions (wash or rub) performed
Denominator (D) Number of opportunities observed
Formula (N/D) x 100
Target ≥75% compliance rate at each audit (quarterly audit)
Data collection at facility Quarterly (every 3 months)
level
Remarks 5 indications have been adopted for the assessment of hand
hygiene performance ‘My 5 Moments for Hand Hygiene’:
x Before patient contact
x Before aseptic task
x After body fluid exposure risk
x After patient contact
x After contact with patient’s surroundings
18