Page 19 - FALL GUIDELINES MOH 2019
P. 19
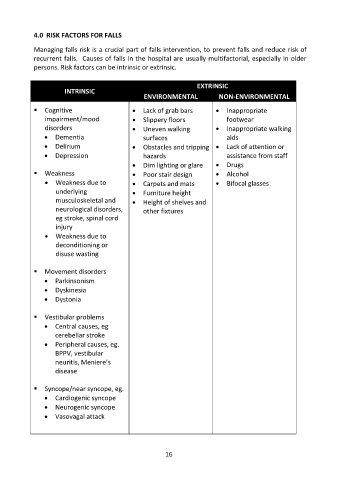
4.0 RISK FACTORS FOR FALLS
Managing falls risk is a crucial part of falls intervention, to prevent falls and reduce risk of
recurrent falls. Causes of falls in the hospital are usually multifactorial, especially in older
persons. Risk factors can be intrinsic or extrinsic.
EXTRINSIC
INTRINSIC
ENVIRONMENTAL NON-ENVIRONMENTAL
Cognitive Lack of grab bars Inappropriate
impairment/mood Slippery floors footwear
disorders Uneven walking Inappropriate walking
Dementia surfaces aids
Delirium Obstacles and tripping Lack of attention or
Depression hazards assistance from staff
Dim lighting or glare Drugs
Weakness Poor stair design Alcohol
Weakness due to Carpets and mats Bifocal glasses
underlying Furniture height
musculoskeletal and Height of shelves and
neurological disorders, other fixtures
eg stroke, spinal cord
injury
Weakness due to
deconditioning or
disuse wasting
Movement disorders
Parkinsonism
Dyskinesia
Dystonia
Vestibular problems
Central causes, eg
cerebellar stroke
Peripheral causes, eg.
BPPV, vestibular
neuritis, Meniere’s
disease
Syncope/near syncope, eg.
Cardiogenic syncope
Neurogenic syncope
Vasovagal attack
16
16