Page 29 - FALL GUIDELINES MOH 2019
P. 29
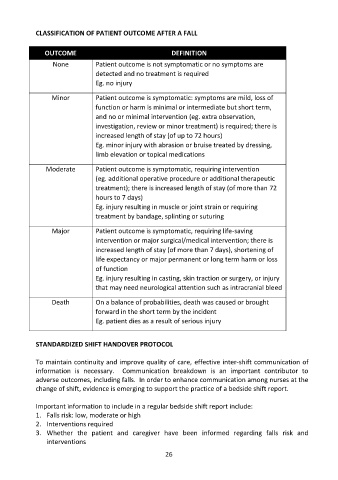
CLASSIFICATION OF PATIENT OUTCOME AFTER A FALL
CLASSIFICATION OF PATIENT OUTCOME AFTER A FALL
OUTCOME DEFINITION
OUTCOME Patient outcome is not symptomatic or no symptoms are
DEFINITION
None
None detected and no treatment is required
Patient outcome is not symptomatic or no symptoms are
Eg. no injury
detected and no treatment is required
Eg. no injury
Minor Patient outcome is symptomatic: symptoms are mild, loss of
Minor Patient outcome is symptomatic: symptoms are mild, loss of
function or harm is minimal or intermediate but short term,
function or harm is minimal or intermediate but short term,
and no or minimal intervention (eg. extra observation,
and no or minimal intervention (eg. extra observation, here is
investigation, review or minor treatment) is required; t
investigation, review or minor treatment) is required; there is
increased length of stay (of up to 72 hours)
increased length of stay (of up to 72 hours)
Eg. minor injury with abrasion or bruise treated by dressing,
limb elevation or topical medications
Eg. minor injury with abrasion or bruise treated by dressing,
limb elevation or topical medications
Moderate Patient outcome is symptomatic, requiring intervention
Moderate Patient outcome is symptomatic, requiring intervention eutic
(eg. additional operative procedure or additional therap
treatment); there is increased length of stay (of more than 72
(eg. additional operative procedure or additional therapeutic
treatment); there is increased length of stay (of more than 72
hours to 7 days)
hours to 7 days)
Eg. injury resulting in muscle or joint strain or requiring
treatment by bandage, splinting or suturing
Eg. injury resulting in muscle or joint strain or requiring
treatment by bandage, splinting or suturing
Major Patient outcome is symptomatic, requiring life-saving
intervention or major surgical/medical intervention; there is
Major Patient outcome is symptomatic, requiring life-saving
intervention or major surgical/medical intervention; there is
increased length of stay (of more than 7 days), shortening of
life expectancy or major permanent or long term harm or loss
increased length of stay (of more than 7 days), shortening of
life expectancy or major permanent or long term harm or loss
of function
of function
Eg. injury resulting in casting, skin traction or surgery, or injury
that may need neurological attention such as intracranial bleed
Eg. injury resulting in casting, skin traction or surgery, or injury
that may need neurological attention such as intracranial bleed
Death On a balance of probabilities, death was caused or brought
On a balance of probabilities, death was caused or brought
Death forward in the short term by the incident
forward in the short term by the incident
Eg. patient dies as a result of serious injury
Eg. patient dies as a result of serious injury
STANDARDIZED SHIFT HANDOVER PROTOCOL
STANDARDIZED SHIFT HANDOVER PROTOCOL
To maintain continuity and improve quality of care, effective inter-shift communication of
information is necessary. Communication breakdown is an important contributor to
To maintain continuity and improve quality of care, effective inter-shift communication of
information is necessary. Communication breakdown is an important contributor to
adverse outcomes, including falls. In order to enhance communication among nurses at the
change of shift, evidence is emerging to support the practice of a bedside shift report.
adverse outcomes, including falls. In order to enhance communication among nurses at the
change of shift, evidence is emerging to support the practice of a bedside shift report.
Important information to include in a regular bedside shift report include:
Important information to include in a regular bedside shift report include:
1. Falls risk: low, moderate or high
2. Interventions required
1. Falls risk: low, moderate or high
2. Interventions required
3. Whether the patient and caregiver have been informed regarding falls risk and
3. Whether the patient and caregiver have been informed regarding falls risk and
interventions
interventions 26
26
26