Page 358 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 358
CHAPTER 18 Dorothy E. Johnson 339
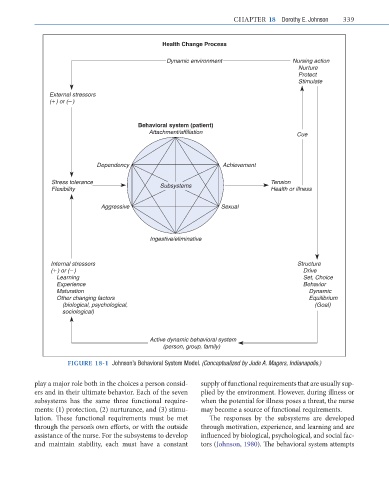
Health Change Process
Dynamic environment Nursing action
Nurture
Protect
Stimulate
External stressors
( ) or ( )
Behavioral system (patient)
Attachment/affiliation Cue
Dependency Achievement
Stress tolerance Tension
Flexibility Subsystems Health or illness
Aggressive Sexual
Ingestive/eliminative
Internal stressors Structure
( ) or ( ) Drive
Learning Set, Choice
Experience Behavior
Maturation Dynamic
Other changing factors Equilibrium
(biological, psychological, (Goal)
sociological)
Active dynamic behavioral system
(person, group, family)
FIGURE 18-1 Johnson’s Behavioral System Model. (Conceptualized by Jude A. Magers, Indianapolis.)
play a major role both in the choices a person consid- supply of functional requirements that are usually sup-
ers and in their ultimate behavior. Each of the seven plied by the environment. However, during illness or
subsystems has the same three functional require- when the potential for illness poses a threat, the nurse
ments: (1) protection, (2) nurturance, and (3) stimu- may become a source of functional requirements.
lation. These functional requirements must be met The responses by the subsystems are developed
through the person’s own efforts, or with the outside through motivation, experience, and learning and are
assistance of the nurse. For the subsystems to develop influenced by biological, psychological, and social fac-
and maintain stability, each must have a constant tors (Johnson, 1980). The behavioral system attempts