Page 109 - DK Children's Encyclopedia
P. 109
Food chains SEE ALSO
▸ ▸ Animal groups
p.22
A food chain is the passing along of energy from food. ▸ ▸ Conservation p.72
Only plants can make their own food. All animals are part ▸ ▸ Eating pp.104—105
of a food chain, either eating plants or other animals. ▸ ▸ Food p.106
All animals need energy to grow, survive, and reproduce. ▸ ▸ Habitats p.126
▸ ▸ Photosynthesis
p.191
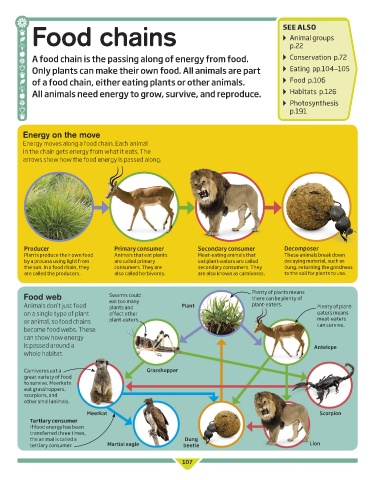
Energy on the move
Energy moves along a food chain. Each animal
in the chain gets energy from what it eats. The
arrows show how the food energy is passed along.
Producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Decomposer
Plants produce their own food Animals that eat plants Meat-eating animals that These animals break down
by a process using light from are called primary eat plant-eaters are called decaying material, such as
the sun. In a food chain, they consumers. They are secondary consumers. They dung, returning the goodness
are called the producers. also called herbivores. are also known as carnivores. to the soil for plants to use.
Plenty of plants means
Food web Swarms could there can be plenty of
eat too many
Animals don’t just feed plants and Plant plant-eaters. Plenty of plant-
on a single type of plant affect other eaters means
or animal, so food chains plant-eaters. meat-eaters
can survive.
become food webs. These
can show how energy
is passed around a Antelope
whole habitat.
Carnivores eat a Grasshopper
great variety of food
to survive. Meerkats
eat grasshoppers,
scorpions, and
other small animals.
Meerkat Scorpion
Tertiary consumer
If food energy has been
transferred three times,
the animal is called a Dung
tertiary consumer. Martial eagle beetle Lion
107
US_107_Food_Chains.indd 107 16/05/2017 09:47