Page 66 - spectroscopic-atlas-5_0-english_Neat
P. 66
Spectroscopic Atlas for Amateur Astronomers 66
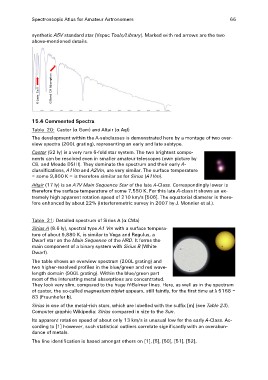
synthetic A5V standard star (Vspec Tools/Library). Marked with red arrows are the two
above-mentioned details.
K-Linie Ca ll
G Band CH Absorption
15.4 Commented Spectra
Table 20: Castor (α Gem) and Altair (α Aql)
The development within the A-subclasses is demonstrated here by a montage of two over-
view spectra (200L grating), representing an early and late subtype.
Castor (52 ly) is a very rare 6-fold star system. The two brightest compo-
nents can be resolved even in smaller amateur telescopes (own picture by
C8, and Meade DSI ll). They dominate the spectrum and their early A-
classifications, A1Vm and A2Vm, are very similar. The surface temperature
– some 9,800 K – is therefore similar as for Sirius (A1Vm).
Altair (17 ly) is an A7V Main Sequence Star of the late A-Class. Correspondingly lower is
therefore the surface temperature of some 7,550 K. For this late A-class it shows an ex-
tremely high apparent rotation speed of 210 km/s [506]. The equatorial diameter is there-
fore enhanced by about 22% (interferometric survey in 2007 by J. Monnier et al.).
Table 21: Detailed spectrum of Sirius A (α CMa)
Sirius A (8.6 ly), spectral type A1 Vm with a surface tempera-
ture of about 9,880 K, is similar to Vega and Regulus, a
Dwarf star on the Main Sequence of the HRD. It forms the
main component of a binary system with Sirius B (White
Dwarf).
The table shows an overview spectrum (200L grating) and
two higher-resolved profiles in the blue/green and red wave-
length domain (900L grating). Within the blue/green part
most of the interesting metal absorptions are concentrated.
They look very slim, compared to the huge H-Balmer lines. Here, as well as in the spectrum
of castor, the so-called magnesium triplet appears, still faintly, for the first time at λ 5168 –
83 (Fraunhofer b).
Sirius is one of the metal-rich stars, which are labelled with the suffix [m] (see Table 23).
Computer graphic Wikipedia: Sirius compared in size to the Sun.
Its apparent rotation speed of about only 13 km/s is unusual low for the early A-Class. Ac-
cording to [1] however, such statistical outliers correlate significantly with an overabun-
dance of metals.
The line identification is based amongst others on [1], [5], [50], [51], [52],