Page 290 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 290
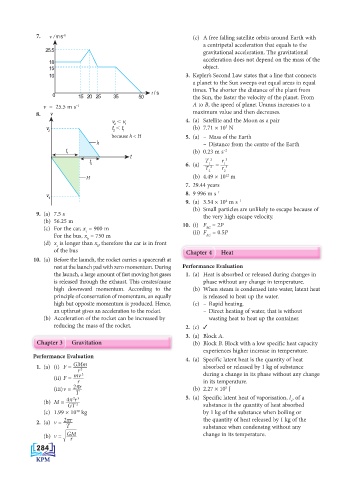
7. v / m s –1 (c) A free falling satellite orbits around Earth with
a centripetal acceleration that equals to the
25.5 gravitational acceleration. The gravitational
18 acceleration does not depend on the mass of the
15 object.
10 3. Kepler’s Second Law states that a line that connects
a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal
0 15 20 25 35 50 t / s times. The shorter the distance of the plant from
the Sun, the faster the velocity of the planet. From
v = 25.5 m s –1 A to B, the speed of planet Uranus increases to a
8. v maximum value and then decreases.
v 2 v 1 4. (a) Satellite and the Moon as a pair
3
v t t (b) 7.71 × 10 N
2 2 1
because h < H 5. (a) – Mass of the Earth
h – Distance from the centre of the Earth
t –2
1 (b) 0.23 m s
t
t T 2 r 3
2 6. (a) 1 = 1
T 2 r 3
2 2
12
H (b) 4.49 × 10 m
7. 29.44 years
v 8. 9 996 m s –1
1
4
9. (a) 3.54 × 10 m s –1
(b) Small particles are unlikely to escape because of
9. (a) 7.5 s
the very high escape velocity.
(b) 56.25 m
10. (i) F = 2P
(c) For the car, x = 900 m BC
c (ii) F = 0.5P
For the bus, x = 750 m AC
b
(d) x is longer than x , therefore the car is in front
c b
of the bus Chapter 4 Heat
10. (a) Before the launch, the rocket carries a spacecraft at
rest at the launch pad with zero momentum. During Performance Evaluation
the launch, a large amount of fast moving hot gases 1. (a) Heat is absorbed or released during changes in
is released through the exhaust. This creates/cause phase without any change in temperature.
high downward momentum. According to the (b) When steam is condensed into water, latent heat
principle of conservation of momentum, an equally is released to heat up the water.
high but opposite momentum is produced. Hence, (c) – Rapid heating.
an upthrust gives an acceleration to the rocket. – Direct heating of water, that is without
(b) Acceleration of the rocket can be increased by wasting heat to heat up the container.
reducing the mass of the rocket. 2. (c) ✓
3. (a) Block A.
Chapter 3 Gravitation (b) Block B. Block with a low specific heat capacity
experiences higher increase in temperature.
Performance Evaluation
4. (a) Specific latent heat is the quantity of heat
GMm
1. (a) (i) F = absorbed or released by 1 kg of substance
r 2
mv 2 during a change in its phase without any change
(ii) F =
r in its temperature.
2πr 5
(iii) v = (b) 2.27 × 10 J
T
2 3
4π r 5. (a) Specific latent heat of vaporisation, l , of a
(b) M = v
GT 2 substance is the quantity of heat absorbed
(c) 1.99 × 10 kg by 1 kg of the substance when boiling or
30
2πr the quantity of heat released by 1 kg of the
2. (a) v =
T substance when condensing without any
GM
(b) v = r change in its temperature.
284
284