Page 89 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 89
Chapter 3
Gravitation
Relating Gravitational Acceleration, g on the Surface of File
the Earth with Universal Gravitational Constant, G
From Newton’s Second Law of
According to Newton’s Second Law of Motion, gravitational force Motion, F = ma.
can be expressed as F = mg. From Newton’s Universal Law of
When involving gravitational
Gm m 2
1
Gravitation, gravitational force is expressed as F = . acceleration, g,
r 2
F = mg
What is the relationship between g and G?
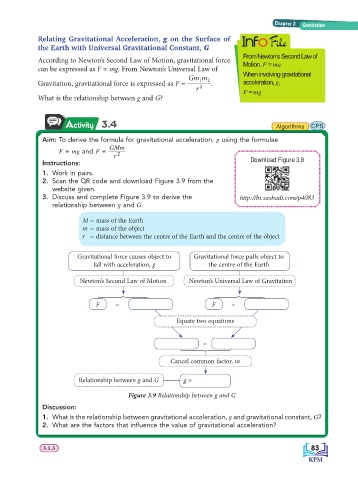
Activity 3.4 Algorithms CPS
Aim: To derive the formula for gravitational acceleration, g using the formulae
GMm
F = mg and F =
r 2
Instructions: Download Figure 3.9
1. Work in pairs.
2. Scan the QR code and download Figure 3.9 from the
website given.
3. Discuss and complete Figure 3.9 to derive the http://bt.sasbadi.com/p4083
relationship between g and G.
M = mass of the Earth
m = mass of the object
r = distance between the centre of the Earth and the centre of the object
Gravitational force causes object to Gravitational force pulls object to
fall with acceleration, g the centre of the Earth
Newton’s Second Law of Motion Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
=
=
F 1442443 F 1442443
Equate two equations
=
1442443
Cancel common factor, m
Relationship between g and G g =
Figure 3.9 Relationship between g and G
Discussion:
1. What is the relationship between gravitational acceleration, g and gravitational constant, G?
2. What are the factors that infl uence the value of gravitational acceleration?
83
83
83
3.1.3 83
3.1.3