Page 214 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 214
THE HUMAN BODY
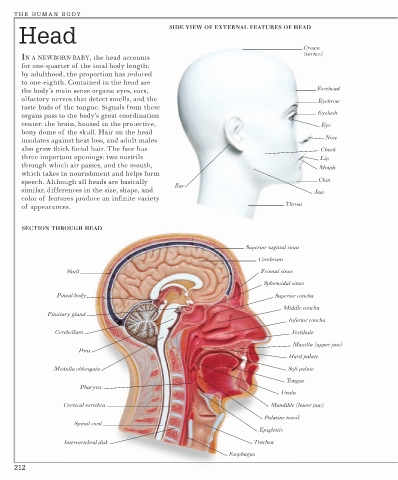
SIDE VIEW OF EXTERNAL FEATURES OF HEAD
Head
Crown
(vertex)
IN A NEWBORN BABY, the head accounts
for one-quarter of the total body length;
by adulthood, the proportion has reduced
to one-eighth. Contained in the head are
the body’s main sense organs: eyes, ears, Forehead
olfactory nerves that detect smells, and the Eyebrow
taste buds of the tongue. Signals from these
Eyelash
organs pass to the body’s great coordination
center: the brain, housed in the protective, Eye
bony dome of the skull. Hair on the head
Nose
insulates against heat loss, and adult males
also grow thick facial hair. The face has Cheek
three important openings: two nostrils Lip
through which air passes, and the mouth,
Mouth
which takes in nourishment and helps form
speech. Although all heads are basically Chin
Ear
similar, differences in the size, shape, and Jaw
color of features produce an infinite variety
Throat
of appearances.
SECTION THROUGH HEAD
Superior sagittal sinus
Cerebrum
Skull Frontal sinus
Sphenoidal sinus
Pineal body Superior concha
Middle concha
Pituitary gland
Inferior concha
Cerebellum Vestibule
Maxilla (upper jaw)
Pons
Hard palate
Medulla oblongata Soft palate
Tongue
Pharynx
Uvula
Cervical vertebra Mandible (lower jaw)
Palatine tonsil
Spinal cord
Epiglottis
Intervertebral disk Trachea
Esophagus
212