Page 228 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 228
THE HUMAN BODY
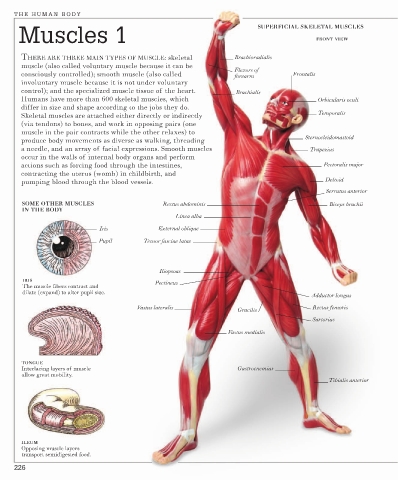
Muscles 1 SUPERFICIAL SKELETAL MUSCLES
FRONT VIEW
THERE ARE THREE MAIN TYPES OF MUSCLE: skeletal Brachioradialis
muscle (also called voluntary muscle because it can be
Flexors of
consciously controlled); smooth muscle (also called forearm Frontalis
involuntary muscle because it is not under voluntary
control); and the specialized muscle tissue of the heart. Brachialis
Humans have more than 600 skeletal muscles, which Orbicularis oculi
differ in size and shape according to the jobs they do.
Temporalis
Skeletal muscles are attached either directly or indirectly
(via tendons) to bones, and work in opposing pairs (one
muscle in the pair contracts while the other relaxes) to
Sternocleidomastoid
produce body movements as diverse as walking, threading
a needle, and an array of facial expressions. Smooth muscles Trapezius
occur in the walls of internal body organs and perform
actions such as forcing food through the intestines, Pectoralis major
contracting the uterus (womb) in childbirth, and
pumping blood through the blood vessels. Deltoid
Serratus anterior
SOME OTHER MUSCLES Rectus abdominis Biceps brachii
IN THE BODY
Linea alba
Iris External oblique
Pupil Tensor fasciae latae
Iliopsoas
IRIS Pectineus
The muscle fibers contract and
dilate (expand) to alter pupil size.
Adductor longus
Vastus lateralis Rectus femoris
Gracilis
Sartorius
Vastus medialis
TONGUE
Interlacing layers of muscle Gastrocnemius
allow great mobility.
Tibialis anterior
ILEUM
Opposing muscle layers
transport semidigested food.
226