Page 348 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 348
RAIL AND ROAD
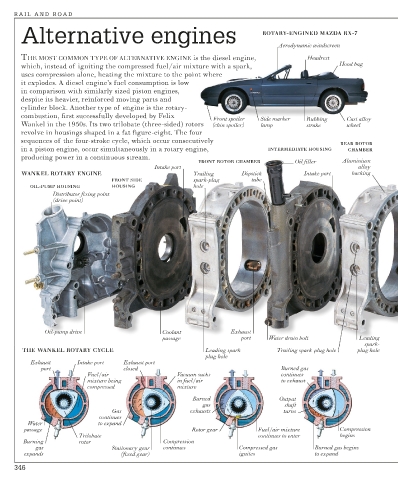
Alternative engines ROTARY-ENGINED MAZDA RX-7
Aerodynamic windscreen
THE MOST COMMON TYPE OF ALTERNATIVE ENGINE is the diesel engine, Headrest
which, instead of igniting the compressed fuel/air mixture with a spark, Hood bag
uses compression alone, heating the mixture to the point where
it explodes. A diesel engine’s fuel consumption is low
in comparison with similarly sized piston engines,
despite its heavier, reinforced moving parts and
cylinder block. Another type of engine is the rotary-
combustion, first successfully developed by Felix
Front spoiler Side marker Rubbing Cast alloy
Wankel in the 1950s. Its two trilobate (three-sided) rotors (chin spoiler) lamp strake wheel
revolve in housings shaped in a fat figure-eight. The four
sequences of the four-stroke cycle, which occur consecutively
REAR ROTOR
in a piston engine, occur simultaneously in a rotary engine, INTERMEDIATE HOUSING CHAMBER
producing power in a continuous stream.
FRONT ROTOR CHAMBER Oil filler Aluminium
Intake port alloy
WANKEL ROTARY ENGINE Trailing Dipstick Intake port backing
FRONT SIDE spark-plug tube
OIL-PUMP HOUSING HOUSING hole
Distributor fixing point
(drive point)
Oil-pump drive Coolant Exhaust
passage port Water drain bolt Leading
spark-
THE WANKEL ROTARY CYCLE Leading spark- Trailing spark-plug hole plug hole
plug hole
Exhaust Intake port Exhaust port
port closed Burned gas
Fuel/air Vacuum sucks continues
mixture being in fuel/air to exhaust
compressed mixture
Burned Output
gas shaft
Gas exhausts turns
continues
Water to expand
passage Rotor gear Fuel/air mixture Compression
Trilobate continues to enter begins
Burning rotor Compression
gas Stationary gear continues Compressed gas Burned gas begins
expands (fixed gear) ignites to expand
346