Page 368 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 368
RAIL AND ROAD
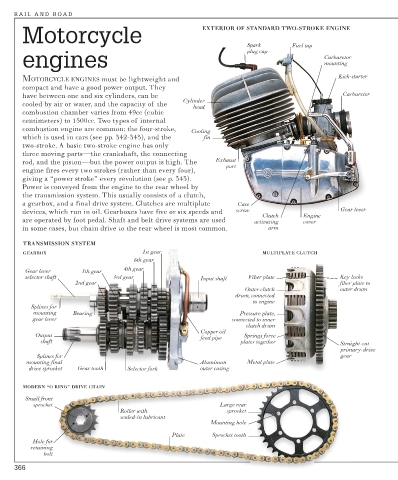
Motorcycle EXTERIOR OF STANDARD TWO-STROKE ENGINE
Spark Fuel tap
plug cap
engines Carburetor
mounting
Kick-starter
MOTORCYCLE ENGINES must be lightweight and
compact and have a good power output. They
have between one and six cylinders, can be Carburetor
Cylinder
cooled by air or water, and the capacity of the
head
combustion chamber varies from 49cc (cubic
centimeters) to 1500cc. Two types of internal
combustion engine are common: the four-stroke, Cooling
which is used in cars (see pp. 342-343), and the fin
two-stroke. A basic two-stroke engine has only
three moving parts—the crankshaft, the connecting
rod, and the piston—but the power output is high. The Exhaust
port
engine fires every two strokes (rather than every four),
giving a “power stroke” every revolution (see p. 343).
Power is conveyed from the engine to the rear wheel by
the transmission system. This usually consists of a clutch,
a gearbox, and a final drive system. Clutches are multiplate Case
devices, which run in oil. Gearboxes have five or six speeds and screw Gear lever
Clutch Engine
are operated by foot pedal. Shaft and belt drive systems are used activating cover
in some cases, but chain drive to the rear wheel is most common. arm
TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
GEARBOX 1st gear MULTIPLATE CLUTCH
6th gear
4th gear
Gear lever 5th gear
selector shaft 3rd gear Input shaft Fiber plate Key locks
2nd gear fiber plate to
Outer clutch outer drum
drum, connected
to engine
Splines for
mounting Bearing Pressure plate,
gear lever connected to inner
clutch drum
Copper oil
Output feed pipe Springs force
shaft plates together Straight-cut
primary-drive
Splines for gear
mounting final Aluminum Metal plate
drive sprocket Gear tooth Selector fork outer casing
MODERN “O RING” DRIVE CHAIN
Small front
sprocket Large rear
Roller with sprocket
sealed-in lubricant
Mounting hole
Plate Sprocket tooth
Hole for
retaining
bolt
366