Page 420 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 420
SEA AND AIR
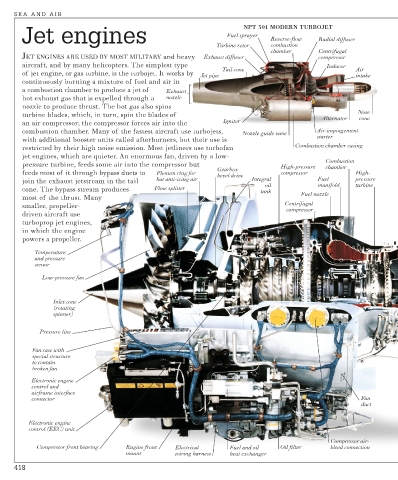
NPT 301 MODERN TURBOJET
Jet engines Fuel sprayer Reverse-flow Radial diffuser
Turbine rotor combustion
chamber Centrifugal
JET ENGINES ARE USED BY MOST MILITARY and heavy Exhaust diffuser compressor
aircraft, and by many helicopters. The simplest type Inducer
Tail cone Air
of jet engine, or gas turbine, is the turbojet. It works by Jet pipe intake
continuously burning a mixture of fuel and air in
a combustion chamber to produce a jet of Exhaust
hot exhaust gas that is expelled through a nozzle
nozzle to produce thrust. The hot gas also spins
Nose
turbine blades, which, in turn, spin the blades of Alternator cone
an air compressor; the compressor forces air into the Igniter
combustion chamber. Many of the fastest aircraft use turbojets, Nozzle guide vane Air impingement
with additional booster units called afterburners, but their use is starter
Combustion chamber casing
restricted by their high noise emission. Most jetliners use turbofan
jet engines, which are quieter. An enormous fan, driven by a low-
Combustion
pressure turbine, feeds some air into the compressor but High-pressure chamber
Gearbox
feeds most of it through bypass ducts to Plenum ring for bevel drive compressor High-
join the exhaust jetstream in the tail hot anti-icing air Integral Fuel pressure
oil manifold turbine
cone. The bypass stream produces Flow splitter tank
most of the thrust. Many Fuel nozzle
smaller, propeller- Centrifugal
compressor
driven aircraft use
turboprop jet engines,
in which the engine
powers a propeller.
Temperature
and pressure
sensor
Low-pressure fan
Inlet cone
(rotating
spinner)
Pressure line
Fan case with
special structure
to contain
broken fan
Electronic engine
control and
airframe interface
connector Fan
duct
Electronic engine
control (EEC) unit
Compressor air-
Compressor front bearing Engine front Electrical Fuel and oil Oil filter bleed connection
mount wiring harness heat exchanger
418