Page 124 - World of Animals - Book of Sharks & Ocean Predators
P. 124
Sharks & Ocean Predators
WorldMags.net
Anatomy of the world’s largest reptile
Saltwater crocodiles are extremely successful
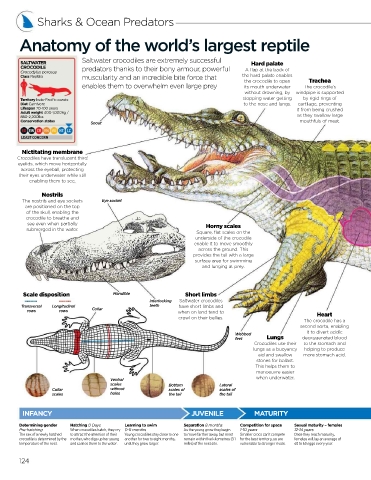
SALTWATER Hard palate
CROCODILE predators thanks to their bony armour, powerful A flap at the back of
Crocodylus porosus
Class Reptilia muscularity and an incredible bite force that the hard palate enables
the crocodile to open Trachea
enables them to overwhelm even large prey its mouth underwater The crocodile’s
without drowning, by windpipe is supported
Territory Indo-Pacifi c coasts stopping water getting by rigid rings of
Diet Carnivore to the nose and lungs. cartilage, preventing
Lifespan 70-100 years it from being crushed
Adult weight 400-1,000kg /
880-2,200lbs as they swallow large
Conservation status mouthfuls of meat.
Snout
LEAST CONCERN
Nictitating membrane
Crocodiles have translucent third
eyelids, which move horizontally
across the eyeball, protecting
their eyes underwater while still
enabling them to see.
Nostrils
The nostrils and eye sockets Eye socket
are positioned on the top
of the skull, enabling the
crocodile to breathe and
see even when partially
submerged in the water. Horny scales
Square, flat scales on the
underside of the crocodile
enable it to move smoothly
across the ground. This
provides the tail with a large
surface area for swimming
and lunging at prey.
Scale disposition Mandible Short limbs
Interlocking Saltwater crocodiles
Transversal Longitudinal teeth have short limbs and
rows rows Collar when on land tend to
crawl on their bellies. Heart
The crocodile has a
second aorta, enabling
it to divert acidic
Webbed
feet Lungs deoxygenated blood
Crocodiles use their to the stomach and
lungs as a buoyancy helping to produce
aid and swallow more stomach acid.
stones for ballast.
This helps them to
manoeuvre easier
when underwater.
Ventral
scales Bottom Lateral
Collar without scales of scales of
scales holes the tail the tail
INFANCY JUVENILE MATURITY
Determining gender Hatching 0 Days Learning to swim Separation 8 months Competition for space Sexual maturity – females
Pre-hatching When crocodiles hatch, they cry 0-8 months As the young grow they begin 1-10 years 12-14 years
The sex of a newly hatched to attract the attention of their Young crocodiles stay close to one to move farther away, but most Smaller crocs can’t compete Once they reach maturity,
crocodile is determined by the mother, who digs up her young another for two to eight months, remain within five kilometres (3.1 for the best territory, so are females will lay an average of
temperature of the nest. and carries them to the water. until they grow larger. miles) of the nest site. vulnerable to stronger rivals. 40 to 60 eggs every year.
124
WorldMags.net
WorldMags.net