Page 6 - REC :: M.E. CS Curriculum and Syllabus - R2019
P. 6
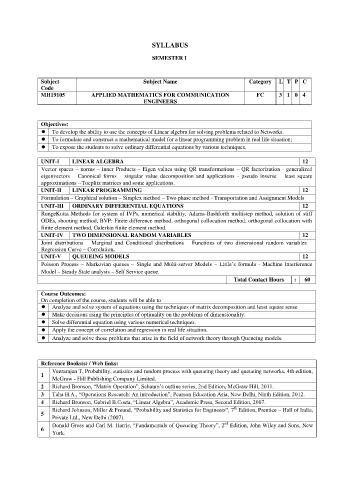
SYLLABUS
SEMESTER I
Subject Subject Name Category L T P C
Code
MH19105 APPLIED MATHEMATICS FOR COMMUNICATION FC 3 1 0 4
ENGINEERS
Objectives:
To develop the ability to use the concepts of Linear algebra for solving problems related to Networks.
To formulate and construct a mathematical model for a linear programming problem in real life situation;
To expose the students to solve ordinary differential equations by various techniques.
UNIT-I LINEAR ALGEBRA 12
Vector spaces – norms – Inner Products – Eigen values using QR transformations – QR factorization - generalized
eigenvectors – Canonical forms – singular value decomposition and applications - pseudo inverse – least square
approximations --Toeplitz matrices and some applications.
UNIT-II LINEAR PROGRAMMING 12
Formulation – Graphical solution – Simplex method – Two phase method - Transportation and Assignment Models
UNIT-III ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 12
RungeKutta Methods for system of IVPs, numerical stability, Adams-Bashforth multistep method, solution of stiff
ODEs, shooting method, BVP: Finite difference method, orthogonal collocation method, orthogonal collocation with
finite element method, Galerkin finite element method.
UNIT-IV TWO DIMENSIONAL RANDOM VARIABLES 12
Joint distributions – Marginal and Conditional distributions – Functions of two dimensional random variables –
Regression Curve – Correlation.
UNIT-V QUEUEING MODELS 12
Poisson Process – Markovian queues – Single and Multi-server Models – Little‟s formula - Machine Interference
Model – Steady State analysis – Self Service queue.
Total Contact Hours : 60
Course Outcomes:
On completion of the course, students will be able to
Analyze and solve system of equations using the techniques of matrix decomposition and least square sense
Make decisions using the principles of optimality on the problems of dimensionality.
Solve differential equation using various numerical techniques.
Apply the concept of correlation and regression in real life situation.
Analyze and solve those problems that arise in the field of network theory through Queueing models.
Reference Books(s) / Web links:
Veerarajan T, Probability, statistics and random process with queueing theory and queueing networks, 4th edition,
1
McGraw - Hill Publishing Company Limited.
2 Richard Bronson, “Matrix Operation”, Schaum‟s outline series, 2nd Edition, McGraw Hill, 2011.
3 Taha H.A., “Operations Research: An introduction”, Pearson Education Asia, New Delhi, Ninth Edition, 2012.
4 Richard Bronson, Gabriel B.Costa, “Linear Algebra”, Academic Press, Second Edition, 2007.
th
Richard Johnson, Miller & Freund, “Probability and Statistics for Engineers”, 7 Edition, Prentice – Hall of India,
5
Private Ltd., New Delhi (2007).
nd
Donald Gross and Carl M. Harris, “Fundamentals of Queueing Theory”, 2 Edition, John Wiley and Sons, New
6
York.