Page 24 - REC :: MBA CURRICULUM AND SYLLABUS :: R2019
P. 24
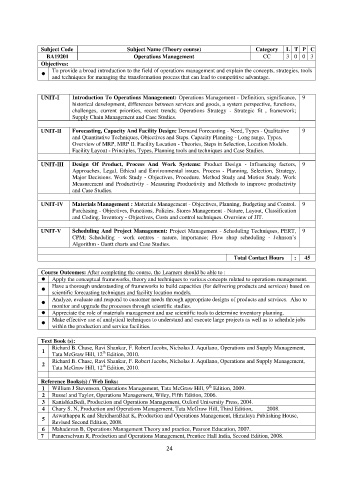
Subject Code Subject Name (Theory course) Category L T P C
BA19201 Operations Management CC 3 0 0 3
Objectives:
To provide a broad introduction to the field of operations management and explain the concepts, strategies, tools
and techniques for managing the transformation process that can lead to competitive advantage.
UNIT-I Introduction To Operations Management: Operations Management - Definition, significance, 9
historical development, differences between services and goods, a system perspective, functions,
challenges, current priorities, recent trends; Operations Strategy - Strategic fit , framework;
Supply Chain Management and Case Studies.
UNIT-II Forecasting, Capacity And Facility Design: Demand Forecasting - Need, Types - Qualitative 9
and Quantitative Techniques, Objectives and Steps. Capacity Planning - Long range, Types,
Overview of MRP, MRP II. Facility Location - Theories, Steps in Selection, Location Models.
Facility Layout - Principles, Types, Planning tools and techniques and Case Studies.
UNIT-III Design Of Product, Process And Work Systems: Product Design - Influencing factors, 9
Approaches, Legal, Ethical and Environmental issues. Process - Planning, Selection, Strategy,
Major Decisions. Work Study - Objectives, Procedure. Method Study and Motion Study. Work
Measurement and Productivity - Measuring Productivity and Methods to improve productivity
and Case Studies.
UNIT-IV Materials Management : Materials Management - Objectives, Planning, Budgeting and Control. 9
Purchasing - Objectives, Functions, Policies. Stores Management - Nature, Layout, Classification
and Coding. Inventory - Objectives, Costs and control techniques. Overview of JIT.
UNIT-V Scheduling And Project Management: Project Management - Scheduling Techniques, PERT, 9
CPM; Scheduling - work centres - nature, importance; Flow shop scheduling - Johnson’s
Algorithm - Gantt charts and Case Studies.
Total Contact Hours : 45
Course Outcomes: After completing the course, the Learners should be able to :
Apply the conceptual frameworks, theory and techniques to various concepts related to operations management.
Have a thorough understanding of frameworks to build capacities (for delivering products and services) based on
scientific forecasting techniques and facility location models.
Analyze, evaluate and respond to customer needs through appropriate designs of products and services. Also to
monitor and upgrade the processes through scientific studies.
Appreciate the role of materials management and use scientific tools to determine inventory planning.
Make effective use of analytical techniques to understand and execute large projects as well as to schedule jobs
within the production and service facilities.
Text Book (s):
Richard B. Chase, Ravi Shankar, F. Robert Jacobs, Nicholas J. Aquilano, Operations and Supply Management,
1 th
Tata McGraw Hill, 12 Edition, 2010.
Richard B. Chase, Ravi Shankar, F. Robert Jacobs, Nicholas J. Aquilano, Operations and Supply Management,
2
th
Tata McGraw Hill, 12 Edition, 2010.
Reference Books(s) / Web links:
th
1 William J Stevenson, Operations Management, Tata McGraw Hill, 9 Edition, 2009.
2 Russel and Taylor, Operations Management, Wiley, Fifth Edition, 2006.
3 KanishkaBedi, Production and Operations Management, Oxford University Press, 2004.
4 Chary S. N, Production and Operations Management, Tata McGraw Hill, Third Edition, 2008.
Aswathappa K and ShridharaBhat K, Production and Operations Management, Himalaya Publishing House,
5
Revised Second Edition, 2008.
6 Mahadevan B, Operations Management Theory and practice, Pearson Education, 2007.
7 Pannerselvam R, Production and Operations Management, Prentice Hall India, Second Edition, 2008.
24