Page 40 - REC :: M.E. CSE Curriculum and Syllabus - R2019
P. 40
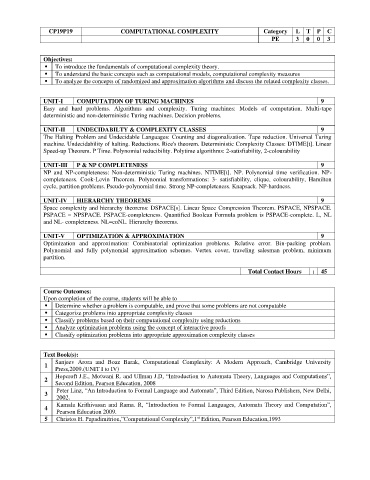
CP19P19 COMPUTATIONAL COMPLEXITY Category L T P C
PE 3 0 0 3
Objectives:
⚫ To introduce the fundamentals of computational complexity theory.
⚫ To understand the basic concepts such as computational models, computational complexity measures
⚫ To analyze the concepts of randomized and approximation algorithms and discuss the related complexity classes.
UNIT-I COMPUTATION OF TURING MACHINES 9
Easy and hard problems. Algorithms and complexity. Turing machines: Models of computation. Multi-tape
deterministic and non-deterministic Turing machines. Decision problems.
UNIT-II UNDECIDABILTY & COMPLEXITY CLASSES 9
The Halting Problem and Undecidable Languages: Counting and diagonalization. Tape reduction. Universal Turing
machine. Undecidability of halting. Reductions. Rice's theorem. Deterministic Complexity Classes: DTIME[t]. Linear
Speed-up Theorem. P Time. Polynomial reducibility. Polytime algorithms: 2-satisfiability, 2-colourability
UNIT-III P & NP COMPLETENESS 9
NP and NP-completeness: Non-deterministic Turing machines. NTIME[t]. NP. Polynomial time verification. NP-
completeness. Cook-Levin Theorem. Polynomial transformations: 3- satisfiability, clique, colourability, Hamilton
cycle, partition problems. Pseudo-polynomial time. Strong NP-completeness. Knapsack. NP-hardness.
UNIT-IV HIERARCHY THEOREMS 9
Space complexity and hierarchy theorems: DSPACE[s]. Linear Space Compression Theorem. PSPACE, NPSPACE.
PSPACE = NPSPACE. PSPACE-completeness. Quantified Boolean Formula problem is PSPACE-complete. L, NL
and NL- completeness. NL=coNL. Hierarchy theorems.
UNIT-V OPTIMIZATION & APPROXIMATION 9
Optimization and approximation: Combinatorial optimization problems. Relative error. Bin-packing problem.
Polynomial and fully polynomial approximation schemes. Vertex cover, traveling salesman problem, minimum
partition.
Total Contact Hours : 45
Course Outcomes:
Upon completion of the course, students will be able to
⚫ Determine whether a problem is computable, and prove that some problems are not computable
⚫ Categorize problems into appropriate complexity classes
⚫ Classify problems based on their computational complexity using reductions
⚫ Analyze optimization problems using the concept of interactive proofs
⚫ Classify optimization problems into appropriate approximation complexity classes
Text Book(s):
Sanjeev Arora and Boaz Barak, Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach, Cambridge University
1
Press,2009.(UNIT I to IV)
Hopcroft J.E., Motwani R. and Ullman J.D, “Introduction to Automata Theory, Languages and Computations”,
2
Second Edition, Pearson Education, 2008
Peter Linz, “An Introduction to Formal Language and Automata”, Third Edition, Narosa Publishers, New Delhi,
3
2002.
Kamala Krithivasan and Rama. R, “Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata Theory and Computation”,
4
Pearson Education 2009.
st
5 Christos H. Papadimitriou,”Computational Complexity”,1 Edition, Pearson Education,1993