Page 37 - REC :: M.E. CSE Curriculum and Syllabus - R2019
P. 37
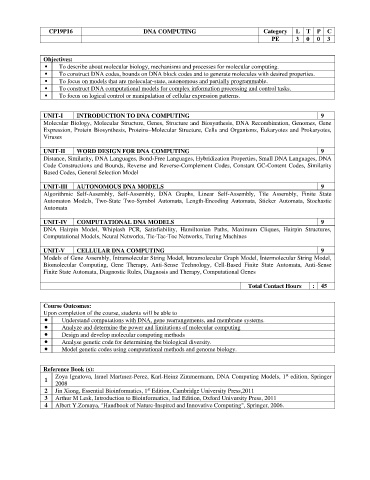
CP19P16 DNA COMPUTING Category L T P C
PE 3 0 0 3
Objectives:
⚫ To describe about molecular biology, mechanisms and processes for molecular computing.
⚫ To construct DNA codes, bounds on DNA block codes and to generate molecules with desired properties.
⚫ To focus on models that are molecular-state, autonomous and partially programmable.
⚫ To construct DNA computational models for complex information processing and control tasks.
⚫ To focus on logical control or manipulation of cellular expression patterns.
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION TO DNA COMPUTING 9
Molecular Biology, Molecular Structure, Genes, Structure and Biosynthesis, DNA Recombination, Genomes, Gene
Expression, Protein Biosynthesis, Proteins–Molecular Structure, Cells and Organisms, Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes,
Viruses
UNIT-II WORD DESIGN FOR DNA COMPUTING 9
Distance, Similarity, DNA Languages, Bond-Free Languages, Hybridization Properties, Small DNA Languages, DNA
Code Constructions and Bounds, Reverse and Reverse-Complement Codes, Constant GC-Content Codes, Similarity
Based Codes, General Selection Model
UNIT-III AUTONOMOUS DNA MODELS 9
Algorithmic Self-Assembly, Self-Assembly, DNA Graphs, Linear Self-Assembly, Tile Assembly, Finite State
Automaton Models, Two-State Two-Symbol Automata, Length-Encoding Automata, Sticker Automata, Stochastic
Automata
UNIT-IV COMPUTATIONAL DNA MODELS 9
DNA Hairpin Model, Whiplash PCR, Satisfiability, Hamiltonian Paths, Maximum Cliques, Hairpin Structures,
Computational Models, Neural Networks, Tic-Tac-Toe Networks, Turing Machines
UNIT-V CELLULAR DNA COMPUTING 9
Models of Gene Assembly, Intramolecular String Model, Intramolecular Graph Model, Intermolecular String Model,
Biomolecular Computing, Gene Therapy, Anti-Sense Technology, Cell-Based Finite State Automata, Anti-Sense
Finite State Automata, Diagnostic Rules, Diagnosis and Therapy, Computational Genes
Total Contact Hours : 45
Course Outcomes:
Upon completion of the course, students will be able to
⚫ Understand computations with DNA, gene rearrangements, and membrane systems.
⚫ Analyze and determine the power and limitations of molecular computing
⚫ Design and develop molecular computing methods
⚫ Analyse genetic code for determining the biological diversity.
⚫ Model genetic codes using computational methods and genome biology.
Reference Book (s):
st
Zoya Ignatova, Israel Martınez-Perez, Karl-Heinz Zimmermann, DNA Computing Models, 1 edition, Springer
1
2008
st
2 Jin Xiong, Essential Bioinformatics, 1 Edition, Cambridge University Press,2011
3 Arthur M Lesk, Introduction to Bioinformatics, 1nd Edition, Oxford University Press, 2011
4 Albert Y.Zomaya, "Handbook of Nature-Inspired and Innovative Computing", Springer, 2006.