Page 218 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 218
174 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—Virology Microbiology ` microbiology—Virology
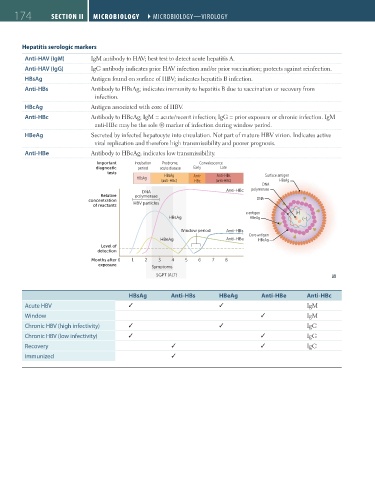
Hepatitis serologic markers
Anti-HAV (IgM) IgM antibody to HAV; best test to detect acute hepatitis A.
Anti-HAV (IgG) IgG antibody indicates prior HAV infection and/or prior vaccination; protects against reinfection.
HBsAg Antigen found on surface of HBV; indicates hepatitis B infection.
Anti-HBs Antibody to HBsAg; indicates immunity to hepatitis B due to vaccination or recovery from
infection.
HBcAg Antigen associated with core of HBV.
Anti-HBc Antibody to HBcAg; IgM = acute/recent infection; IgG = prior exposure or chronic infection. IgM
anti-HBc may be the sole ⊕ marker of infection during window period.
HBeAg Secreted by infected hepatocyte into circulation. Not part of mature HBV virion. Indicates active
viral replication and therefore high transmissibility and poorer prognosis.
Anti-HBe Antibody to HBeAg; indicates low transmissibility.
Important Incubation Prodrome, Convalescence
diagnostic period acute disease Early Late
tests HBsAg Anti-HBs Surface antigen
HBsAg Anti-
(anti-HBc) HBc (anti-HBc) HBsAg
DNA
DNA Anti-HBc polymerase
Relative polymerase
concentration HBV particles DNA
of reactants
e antigen (+)
HBsAg HBeAg (–)
Window period Anti-HBs
Core antigen
HBeAg Anti-HBe HBcAg
Level of
detection
Months after 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
exposure Symptoms
SGPT (ALT)
HBsAg Anti-HBs HBeAg Anti-HBe Anti-HBc
Acute HBV ✓ ✓ IgM
Window ✓ IgM
Chronic HBV (high infectivity) ✓ ✓ IgG
Chronic HBV (low infectivity) ✓ ✓ IgG
Recovery ✓ ✓ IgG
Immunized ✓
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 174 11/14/19 12:22 PM