Page 285 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 285
Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS SEcTIoN II 241
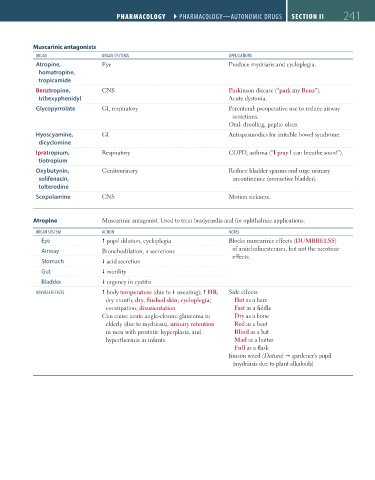
Muscarinic antagonists
dRUGS ORGAN SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS
Atropine, Eye Produce mydriasis and cycloplegia.
homatropine,
tropicamide
Benztropine, CNS Parkinson disease (“park my Benz”).
trihexyphenidyl Acute dystonia.
Glycopyrrolate GI, respiratory Parenteral: preoperative use to reduce airway
secretions.
Oral: drooling, peptic ulcer.
Hyoscyamine, GI Antispasmodics for irritable bowel syndrome.
dicyclomine
Ipratropium, Respiratory COPD, asthma (“I pray I can breathe soon!”).
tiotropium
Oxybutynin, Genitourinary Reduce bladder spasms and urge urinary
solifenacin, incontinence (overactive bladder).
tolterodine
Scopolamine CNS Motion sickness.
Atropine Muscarinic antagonist. Used to treat bradycardia and for ophthalmic applications.
ORGAN SYSTEM ACTION NOTES
Eye pupil dilation, cycloplegia Blocks muscarinic effects (DUMBBELSS)
Airway Bronchodilation, secretions of anticholinesterases, but not the nicotinic
effects.
Stomach acid secretion
Gut motility
Bladder urgency in cystitis
AdVERSE EFFECTS body temperature (due to sweating); HR; Side effects:
dry mouth; dry, flushed skin; cycloplegia; Hot as a hare
constipation; disorientation Fast as a fiddle
Can cause acute angle-closure glaucoma in Dry as a bone
elderly (due to mydriasis), urinary retention Red as a beet
in men with prostatic hyperplasia, and Blind as a bat
hyperthermia in infants. Mad as a hatter
Full as a flask
Jimson weed (Datura) gardener’s pupil
(mydriasis due to plant alkaloids)
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 241 11/7/19 4:08 PM