Page 290 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 290
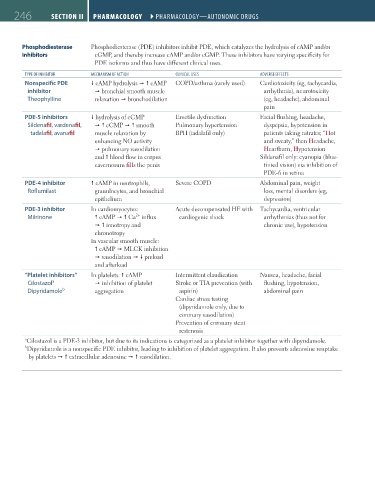
246 SEcTIoN II Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—AUTONOMIC dRUGS
Phosphodiesterase Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors inhibit PDE, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of cAMP and/or
inhibitors cGMP, and thereby increase cAMP and/or cGMP. These inhibitors have varying specificity for
PDE isoforms and thus have different clinical uses.
TYPE OF INHIBITOR MECHANISM OF ACTION CLINICAL USES AdVERSE EFFECTS
Nonspecific PDE cAMP hydrolysis cAMP COPD/asthma (rarely used) Cardiotoxicity (eg, tachycardia,
inhibitor bronchial smooth muscle arrhythmia), neurotoxicity
Theophylline relaxation bronchodilation (eg, headache), abdominal
pain
PDE-5 inhibitors hydrolysis of cGMP Erectile dysfunction Facial flushing, headache,
Sildenafil, vardenafil, cGMP smooth Pulmonary hypertension dyspepsia, hypotension in
tadalafil, avanafil muscle relaxation by BPH (tadalafil only) patients taking nitrates; “Hot
enhancing NO activity and sweaty,” then Headache,
pulmonary vasodilation Heartburn, Hypotension
and blood flow in corpus Sildenafil only: cyanopia (blue-
cavernosum fills the penis tinted vision) via inhibition of
PDE-6 in retina
PDE-4 inhibitor cAMP in neutrophils, Severe COPD Abdominal pain, weight
Roflumilast granulocytes, and bronchial loss, mental disorders (eg,
epithelium depression)
PDE-3 inhibitor In cardiomyocytes: Acute decompensated HF with Tachycardia, ventricular
2+
Milrinone cAMP Ca influx cardiogenic shock arrhythmias (thus not for
ionotropy and chronic use), hypotension
chronotropy
In vascular smooth muscle:
cAMP MLCK inhibition
vasodilation preload
and afterload
“Platelet inhibitors” In platelets: cAMP Intermittent claudication Nausea, headache, facial
Cilostazol a inhibition of platelet Stroke or TIA prevention (with flushing, hypotension,
Dipyridamole b aggregation aspirin) abdominal pain
Cardiac stress testing
(dipyridamole only, due to
coronary vasodilation)
Prevention of coronary stent
restenosis
a Cilostazol is a PDE-3 inhibitor, but due to its indications is categorized as a platelet inhibitor together with dipyridamole.
b Dipyridamole is a nonspecific PDE inhibitor, leading to inhibition of platelet aggregation. It also prevents adenosine reuptake
by platelets extracellular adenosine vasodilation.
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 246 11/7/19 4:08 PM