Page 604 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 604
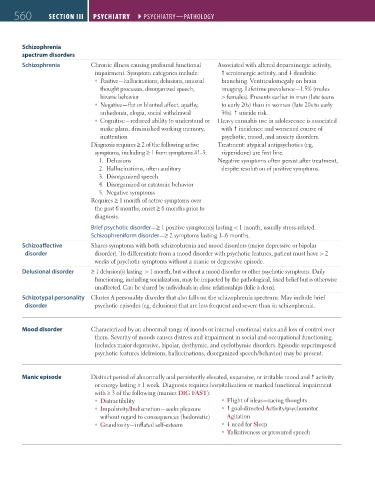
560 sEctiON iii Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology
Schizophrenia
spectrum disorders
Schizophrenia Chronic illness causing profound functional Associated with altered dopaminergic activity,
impairment. Symptom categories include: serotonergic activity, and dendritic
Positive—hallucinations, delusions, unusual branching. Ventriculomegaly on brain
thought processes, disorganized speech, imaging. Lifetime prevalence—1.5% (males
bizarre behavior > females). Presents earlier in men (late teens
Negative—flat or blunted affect, apathy, to early 20s) than in women (late 20s to early
anhedonia, alogia, social withdrawal 30s). suicide risk.
Cognitive—reduced ability to understand or Heavy cannabis use in adolescence is associated
make plans, diminished working memory, with incidence and worsened course of
inattention psychotic, mood, and anxiety disorders.
Diagnosis requires ≥ 2 of the following active Treatment: atypical antipsychotics (eg,
symptoms, including ≥ 1 from symptoms #1–3: risperidone) are first line.
1. Delusions Negative symptoms often persist after treatment,
2. Hallucinations, often auditory despite resolution of positive symptoms.
3. Disorganized speech
4. Disorganized or catatonic behavior
5. Negative symptoms
Requires ≥ 1 month of active symptoms over
the past 6 months; onset ≥ 6 months prior to
diagnosis.
Brief psychotic disorder—≥ 1 positive symptom(s) lasting < 1 month, usually stress-related.
Schizophreniform disorder—≥ 2 symptoms lasting 1–6 months.
Schizoaffective Shares symptoms with both schizophrenia and mood disorders (major depressive or bipolar
disorder disorder). To differentiate from a mood disorder with psychotic features, patient must have > 2
weeks of psychotic symptoms without a manic or depressive episode.
Delusional disorder ≥ 1 delusion(s) lasting > 1 month, but without a mood disorder or other psychotic symptoms. Daily
functioning, including socialization, may be impacted by the pathological, fixed belief but is otherwise
unaffected. Can be shared by individuals in close relationships (folie à deux).
Schizotypal personality Cluster A personality disorder that also falls on the schizophrenia spectrum. May include brief
disorder psychotic episodes (eg, delusions) that are less frequent and severe than in schizophrenia.
Mood disorder Characterized by an abnormal range of moods or internal emotional states and loss of control over
them. Severity of moods causes distress and impairment in social and occupational functioning.
Includes major depressive, bipolar, dysthymic, and cyclothymic disorders. Episodic superimposed
psychotic features (delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech/behavior) may be present.
Manic episode Distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and activity
or energy lasting ≥ 1 week. Diagnosis requires hospitalization or marked functional impairment
with ≥ 3 of the following (manics DIG FAST):
Distractibility Flight of ideas—racing thoughts
Impulsivity/Indiscretion—seeks pleasure goal-directed Activity/psychomotor
without regard to consequences (hedonistic) Agitation
Grandiosity—inflated self-esteem need for Sleep
Talkativeness or pressured speech
FAS1_2019_13-Psych.indd 560 11/7/19 5:28 PM