Page 600 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 600
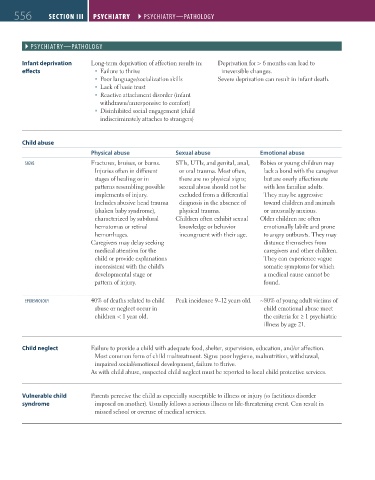
556 sEctiON iii Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology
` Psychiatry—Pathology
Infant deprivation Long-term deprivation of affection results in: Deprivation for > 6 months can lead to
effects Failure to thrive irreversible changes.
Poor language/socialization skills Severe deprivation can result in infant death.
Lack of basic trust
Reactive attachment disorder (infant
withdrawn/unresponsive to comfort)
Disinhibited social engagement (child
indiscriminately attaches to strangers)
Child abuse
Physical abuse Sexual abuse Emotional abuse
sigNs Fractures, bruises, or burns. STIs, UTIs, and genital, anal, Babies or young children may
Injuries often in different or oral trauma. Most often, lack a bond with the caregiver
stages of healing or in there are no physical signs; but are overly affectionate
patterns resembling possible sexual abuse should not be with less familiar adults.
implements of injury. excluded from a differential They may be aggressive
Includes abusive head trauma diagnosis in the absence of toward children and animals
(shaken baby syndrome), physical trauma. or unusually anxious.
characterized by subdural Children often exhibit sexual Older children are often
hematomas or retinal knowledge or behavior emotionally labile and prone
hemorrhages. incongruent with their age. to angry outbursts. They may
Caregivers may delay seeking distance themselves from
medical attention for the caregivers and other children.
child or provide explanations They can experience vague
inconsistent with the child's somatic symptoms for which
developmental stage or a medical cause cannot be
pattern of injury. found.
EPiDEMiology 40% of deaths related to child Peak incidence 9–12 years old. ~80% of young adult victims of
abuse or neglect occur in child emotional abuse meet
children < 1 year old. the criteria for ≥ 1 psychiatric
illness by age 21.
Child neglect Failure to provide a child with adequate food, shelter, supervision, education, and/or affection.
Most common form of child maltreatment. Signs: poor hygiene, malnutrition, withdrawal,
impaired social/emotional development, failure to thrive.
As with child abuse, suspected child neglect must be reported to local child protective services.
Vulnerable child Parents perceive the child as especially susceptible to illness or injury (vs factitious disorder
syndrome imposed on another). Usually follows a serious illness or life-threatening event. Can result in
missed school or overuse of medical services.
FAS1_2019_13-Psych.indd 556 11/7/19 5:28 PM