Page 309 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 309
Mechanical Separations 279
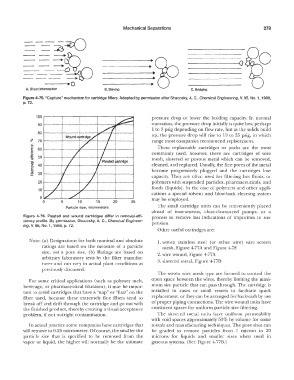
-------Q
A. Direct Interception B. Sieving C. Bridging
Figure 4-75. "Capture" mechanism for cartridge filters. Adapted by permission after Shucosky, A. C., Chemical Engineering, V. 95, No. 1, 1988,
p. 72.
100 pressure drop or lower the holding capacity. In normal
90 operation, the pressure drop initially is quite low, perhaps
1 to 3 psig depending on flow rate, but as the solids build
80
up, the pressure drop will rise to 10 LO 35 psig, in which
,!?.
0 70 range most companies recommend replacement.
� These replaceable cartridges or packs are the most
c:
·u 60 commonly used; however, there are cartridges of wire
Q)
:E 50
(!) mesh, sintered or porous metal which can be removed,
'lij
> 40 cleaned, and replaced. Usually, the fine pores of the metal
0
E become progressively plugged and the cartridges lose
Q)
0: 30
capacity. They are often used for filtering hot fluids, or
20 polymers with suspended particles, pharmaceuticals, and
10 foods (liquids). In the case of polymers and other appli-
cations a special solvent and blow-back cleaning system
may be employed.
Particle size, micrometers The small cartridge units can be conveniently placed
ahead of instruments, close-clearanced pumps, or a
Figure 4-76. Pleated and wound cartridges differ in removal-effi- process to remove last indications of impurities in sus-
ciency profile. By permission, Shucosky, A. C., Chemical Engineer- pension.
ing, V. 95, No. 1, 1988, p. 72.
Other useful cartridges are:
Note: (a) Designations for both nominal and absolute 1. woven stainless steel ( or other wire) wire screen
ratings are based on the measure of a particle mesh, Figure 4-77A and Figure 4-78
size, not a pore size. (b) Ratings are based on 2. wire wound, Figure 4-77 A
arbitrary laboratory tests by the filter manufac- 3. sintered metal, Figure 4-77B
turer and can vary in actual plant conditions as
previously discussed.
The woven wire mesh type are formed to control the
For some critical applications (such as polymer melt, open space between the wires, thereby limiting the maxi-
beverage, or pharmaceutical filtration), it may be impor- mum size particle that can pass through. The cartridge is
tant to avoid cartridges that have a "nap" or "fuzz" on the installed in cases or small vessels Lo facilitate quick
fiber used, because these extremely fine fibers tend to replacement, or they can be arranged for backwash by use
break off and drift through the cartridge and go out with of proper piping connections. The wire wound uni ts have
the finished product, thereby creating a visual acceptance consistent spaces for uniform particle size filtering.
problem, if not outright contamination. The sintered metal units have uniform permeability
with void spaces approximately 50% by volume for some
In actual practice some companies have cartridges that metals and manufacturing techniques. The pore sizes can
will remove to 0.25 micrometer. Of course, the smaller the be graded to remove particles from 1 micron to 20
particle size that is specified to be removed from the microns for liquids and smaller sizes when used in
vapor or liquid, the higher will normally be the ultimate gaseous systems. (See Figure 4-778.)