Page 2 - 1202 Question Bank Additional Mathematics Form 4
P. 2
MUST
KNOW Important Facts
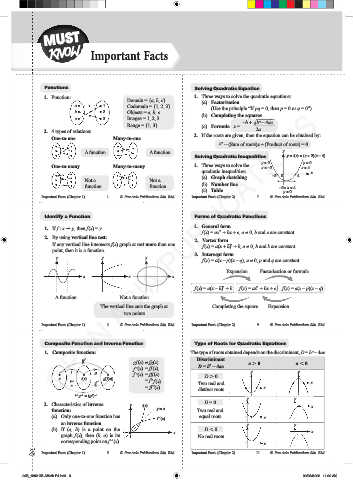
Functions Solving Quadratic Equation
1. Function: 1. Three ways to solve the quadratic equations:
Domain = {a, b, c} (a) Factorisation
a ● ● 1 Codomain = {1, 2, 3} (Use the principle “If pq = 0, then p = 0 or q = 0”)
b ● ● 2 Objects = a, b, c (b) Completing the squares
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
c ● ● 3 Images = 1, 2, 3 2
b – 4ac
Range = {1, 3} (c) Formula x = –b + ABBBBBB
2. 4 types of relations: 2a
One-to-one Many-to-one 2. If the roots are given, then the equation can be obtained by:
x – (Sum of roots)x + (Product of roots) = 0
2
A function A function y
Solving Quadratic Inequalities y = f(x) = (x + 2)(x – 4)
One-to-many Many-to-many 1. Three ways to solve the y > 0 y > 0
quadratic inequalities: x < –2 x > 4
(a) Graph sketching –2 0 4 x
Not a Not a
function function (b) Number line
(c) Table –2< x < 4
y < 0
Important Facts (Chapter 1) 1 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 2) 7 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Identify a Function Forms of Quadratic Functions
1. General form
1. If f : x → y, then f (x) = y.
f (x) = ax + bx + c, a ≠ 0, b and c are constant
2
2. By using vertical line test: 2. Vertex form
If any vertical line intersects f(x) graph at not more than one f (x) = a(x + h) + k, a ≠ 0, h and k are constant
2
point, then it is a function.
3. Intercept form
y y y f (x) = a(x – p)(x – q), a ≠ 0, p and q are constant
Expansion Factorisation or formula
x x x
f (x) = a(x – h) + k f (x) = ax + bx + c f (x) = a(x – p)(x – q)
2
2
A function Not a function
The vertical line cuts the graph at Completing the square Expansion
two points
Important Facts (Chapter 1) 3 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 2) 9 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Composite Function and Inverse Function Type of Roots for Quadratic Equations
1. Composite function: The type of roots obtained depends on the discriminant, D = b – 4ac
2
gf Discriminant
gf (x) ≠ fg(x) a . 0 a , 0
2
f (x) = ff (x), D = b – 4ac
2
3
● f ● g ● f (x) = fff (x) D . 0 y y
x f(x) g[f(x)] = f f (x)
2
f –1 g –1 Two real and x
= ff (x)
2
distinct roots x
f g = (gf ) –1 y y
–1
–1
2. Characteristics of inverse y f(x) D = 0 x
function: y = x Two real and
(a) Only one-to-one function has f (x) equal roots x
–1
an inverse function. y y
(b) If (a, b) is a point on the D , 0 x
graph f (x), then (b, a) is its x No real roots
corresponding point on f (x). x
–1
Important Facts (Chapter 1) 5 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 2) 11 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
00B_1202 QB AMath F4.indd 3 09/05/2022 11:30 AM