Page 4 - 1202 Question Bank Additional Mathematics Form 4
P. 4
1 Functions
Chapter
NOTES
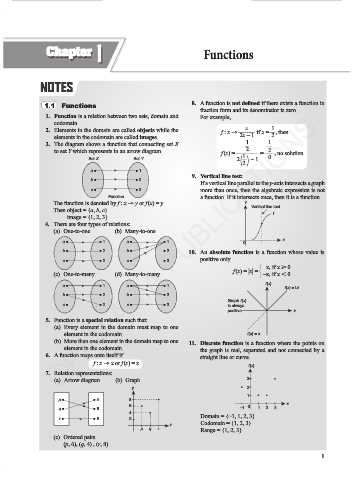
1.1 Functions 8. A function is not defined if there exists a function in
fraction form and its denominator is zero.
1. Function is a relation between two sets, domain and For example,
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
codomain.
1
2. Elements in the domain are called objects while the f : x → x if x = , then
elements in the codomain are called images. 2x – 1 2
3. The diagram shows a function that connecting set X 1 1
to set Y which represents in an arrow diagram. f (x) = 2 = 2 , no solution
1
Set X Set Y 2 1 2 – 1 0
2
a ● ● 1
9. Vertical line test:
b ● ● 2
If a vertical line parallel to the y-axis intersects a graph
c ● ● 3 more than once, then the algebraic expression is not
Function a function. If it intersects once, then it is a function.
The function is denoted by f : x → y or f (x) = y. y
Then object = {a, b, c} Vertical line test
image = {1, 2, 3} f
4. There are four types of relations:
(a) One-to-one (b) Many-to-one
x
a ● ● 1 a ● ● 1 0
b ● ● 2 b ● ● 2 10. An absolute function is a function whose value is
positive only.
c ● ● 3 c ● ● 3
x, if x > 0
(c) One-to-many (d) Many-to-many f (x) = |x| = –x, if x , 0
f(x)
a ● ● 1 a ● ● 1
f(x) = |x|
b ● ● 2 b ● ● 2
Graph f(x)
c ● ● 3 c ● ● 3 is always
positive x
5. Function is a special relation such that:
(a) Every element in the domain must map to one
element in the codomain. f(x) = x
(b) More than one element in the domain map to one 11. Discrete function is a function where the points on
element in the codomain. the graph is real, separated and not connected by a
6. A function maps onto itself if straight line or curve.
f : x → x or f (x) = x f(x)
7. Relation representations:
(a) Arrow diagram (b) Graph 3
y 2
1
p ● ● 4 8
x
6 –1 0 1 2 3
q ● ● 6
4
r ● ● 8 2 Domain = {−1, 1, 2, 3}
x Codomain = {1, 2, 3}
p q r Range = {1, 2, 3}
(c) Ordered pairs
(p, 6), (q, 4) , (r, 8)
1
01_1202 QB AMath F4.indd 1 09/05/2022 11:30 AM