Page 4 - 1202 Question Bank Additional Mathematics Form 5
P. 4
MUST
KNOW Common Mistakes
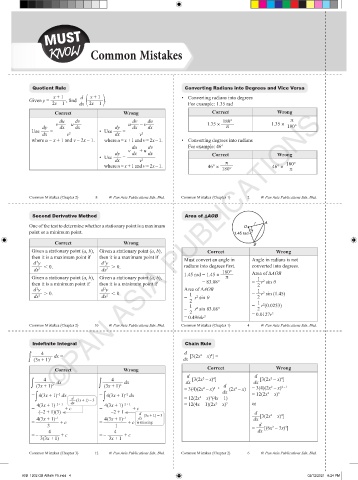
Quotient Rule Converting Radians into Degrees and Vice Versa
x + 1 d x + 1 • Converting radians into degrees
2
1
Given y = —–—–, find —– —–—– .
2x – 1 dx 2x – 1 For example: 1.35 rad
Correct Wrong Correct Wrong
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
du dv dv du 180° π
v—– – u—– u—– – v—– 1.35 × ——– 1.35 × ——–
dy dx dx dy dx dx π 180°
Use —– = —————– • Use —– = —————–
dx v 2 dx v 2
where u = x + 1 and v = 2x – 1. where u = x + 1 and v = 2x – 1. • Converting degrees into radians
du dv For example: 46°
v—– + u—–
dy dx dx Correct Wrong
• Use —– = —————–
dx v 2
180°
π
where u = x + 1 and v = 2x – 1. 46° × ——– 46° × ——–
180°
π
Common Mistakes (Chapter 2) 8 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Common Mistakes (Chapter 1) 2 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Second Derivative Method Area of ∆AOB
One of the test to determine whether a stationary point is a maximum O r A
point or a minimum point. 1.45 rad
Correct Wrong B
Given a stationary point (a, b), Given a stationary point (a, b), Correct Wrong
then it is a maximum point if then it is a maximum point if Must convert an angle in Angle in radians is not
d y d y
2
2
—–– , 0. —–– . 0. radians into degrees first. converted into degrees.
dx 2 dx 2 180° Area of ΔAOB
Given a stationary point (a, b), Given a stationary point (a, b), 1.45 rad = 1.45 × ——– 1
π
2
then it is a minimum point if then it is a minimum point if = 83.08° = —r sin θ
2
d y d y Area of ΔAOB 1
2
2
—–– . 0. —–– , 0. 1 = —r sin (1.45)
2
dx 2 dx 2 = — r sin θ 2
2
2 1
2
1
= — r sin 83.08° = —r (0.0253)
2
2
2 = 0.0127r 2
= 0.4964r 2
Common Mistakes (Chapter 2) 10 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Common Mistakes (Chapter 1) 4 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Indefinite Integral Chain Rule
2
∫ ———— dx = —–[3(2x – x) ] =
d
4
4
2
dx
(3x + 1)
Correct Wrong Correct Wrong
d 2 4 d 2 4
4
4
—–[3(2x – x) ]
2
∫ ———— dx ∫ ———— dx —–[3(2x – x) ] d 2 = 3(4)(2x – x) 4 – 1
2
dx
dx
(3x + 1)
(3x + 1)
2
4 – 1
2
dx
∫
∫
2
= 4(3x + 1) dx = 4(3x + 1) dx = 3(4)(2x – x) —–(2x – x) = 12(2x – x) 3
–2
–2
= 12(2x – x) (4x – 1)
d
2
3
—–(3x + 1) = 3
2
4(3x + 1) –2 + 1 dx 4(3x + 1) –2 + 1 = 12(4x – 1)(2x – x) 3 or
= —————– + c = —————– + c
(–2 + 1)(3) –2 + 1 d d
4
2
4(3x + 1) –1 4(3x + 1) –1 —–(3x + 1) = 3 —–[3(2x – x) ]
dx
dx
= ————– + c = ————– + c is missing
d
–3 –1 = —–[(6x – 3x) ]
2
4
4 4 dx
= – ——–—– + c = – —––— + c
3(3x + 1) 3x + 1
Common Mistakes (Chapter 3) 12 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Common Mistakes (Chapter 2) 6 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
00B_1202 QB AMath F5.indd 4 02/12/2021 8:24 PM