Page 21 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 5 KSSM
P. 21
2+
2+
47. B Copper is the least electropositive metal that has the slowest 4. (a) Zn(s) + Cu (aq) → Zn (aq) + Cu(s)
rate of corrosion. (b) (i) and (ii)
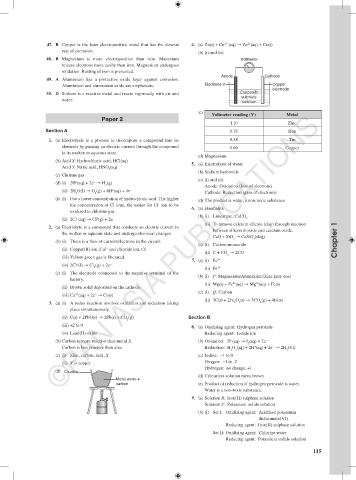
48. B Magnesium is more electropositive than iron. Manesium Voltmeter
release electrons more easily than iron. Magnesium undergoes
oxidation. Rusting of iron is prevented.
Anode Cathode
49. A Aluminium has a protective oxide layer against corrosion.
Aluminium and aluminium oxide are amphoteric. Electrode 2 Copper
electrode
50. D Sodium is a reactive metal and reacts vigorously with air and Copper(II)
sulphate
water. solution
(c)
Voltmeter reading (V) Metal
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Paper 2
1.10 Zinc
Section A 0.78 Iron
1. (a) Electrolysis is a process to decompose a compound into its 0.38 Tin
elements by passing an electric current through the compound 0.00 Copper
in its molten or aqueous state.
(d) Magnesium
(b) Acid X: Hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq)
5. (a) Electrolysis of water
Acid Y: Nitric acid, HNO (aq)
3
(b) Sodium hydroxide
(c) Chorine gas
(c) (i) and (ii)
−
(d) (i) 2H (aq) + 2e → H (g)
+
2 Anode: Oxidation (loss of electrons)
(ii) 2H O(l) → O (g) + 4H (aq) + 4e −
+
2 2 Cathode: Reduction (gain of electrons)
(e) (i) Use a lower concentration of hydrochloric acid. The higher (d) The product is water, a non-toxic substance
the concentration of Cl ions, the easier for Cl ion to be
−
6. (a) Haematite
oxidised to chlorine gas.
(b) (i) Limestone, CaCO
−
2
(ii) 2Cl (aq) → Cl (g) + 2e − 3
(ii) To remove calcium silicate (slag) through reaction
2. (a) Electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric current in
between silicon dioxide and calcium oxide.
the molten or aqueous state and undergo chemical changes.
CaO + SiO → CaSiO (slag)
(b) (i) There is a flow of current/electrons in the circuit. 2 3 Chapter 1
(c) (i) Carbon monoxide
2+
−
(ii) Copper(II) ion, Cu and chloride ion, Cl .
(ii) C + CO → 2CO
(iii) Yellow-green gas is liberated. 2
7. (a) (i) Fe 2+
(iv) 2Cl (l) → Cl (g) + 2e −
−
2 (ii) Fe 3+
(c) (i) The electrode connected to the negative terminal of the
(b) (i) P: Magnesium/Aluminium/Zinc [any one]
battery.
2+
(ii) Mg(s) + Fe (aq) → Mg (aq) + Fe(s)
2+
(ii) Brown solid deposited on the cathode.
(c) (i) Q: Carbon
(iii) Cu (aq) + 2e → Cu(s)
−
2+
(ii) 3C(s) + 2Fe O (s) → 3CO (g) + 4Fe(s)
3. (a) (i) A redox reaction involves oxidation and reduction taking 2 3 2
place simultaneously.
(ii) C(s) + 2PbO(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO (g) Section B
2
(iii) +2 to 0 8. (a) Oxidising agent: Hydrogen peroxide
(iv) Lead(II) oxide Reducing agent: Iodide ion
(b) Carbon is more reactive than metal X. (b) Oxidation: 2I (aq) → I (aq) + 2e
−
−
2
Carbon is less reactive than zinc. Reduction: H O (aq) + 2H (aq) + 2e → 2H O(l)
+
−
2 2 2
(c) (i) Zinc, carbon, lead, X (c) Iodine: −1 to 0
(ii) X is copper Oxygen: −1 to -2
Hydrogen: no change, +1
(d) Crucible
(d) Colourless solution turns brown
Metal oxide +
carbon (e) Product of reduction of hydrogen peroxide is water.
Water is a non-toxic substance.
9. (a) Solution R: Iron(II) sulphate solution
Solution S: Potassium iodide solution
(b) (i) Set I: Oxidising agent: Acidified potassium
dichromate(VI)
Reducing agent: Iron(II) sulphate solution
Set II: Oxidising agent: Chlorine water
Reducing agent: Potassium iodide solution
115