Page 22 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 5 KSSM
P. 22
2+
(ii) Set I: Iron(II) ion, Fe Discussion:
Set II: Iodide ion, I − Potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) solution confirms the
(iii) Set I: Fe (aq) → Fe (aq) + e presence of Fe ions which are produced when iron rusts.
2+
−
2+
3+
−
Set II: 2I (aq) → I (aq) + 2e − The more the dark blue spots formed, the higher the
2
corrosion of iron. Phenolphthalein detects the presence of
OH ions which are produced at the cathode during the
−
Section C corrosion of metals. The higher the intensity of the pink
colour, the greater the extent of rusting of iron. A metal more
10. (a) Iron undergoes oxidation at the anode:
2+
Fe(s)→ Fe (aq) + 2e − electropositive than iron can protect the iron from rusting. A
less electropositive metal than iron speeds up the corrosion
Electrons flow through iron to the cathode (edge of water
of iron.
droplet). Oxygen is reduced to hydroxide ion, OH .
−
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
−
O + 2H O + 4e → 4OH
2 2 11. (a) (i) Solution X in Set I: Dilute hydrochloric acid
−
Fe ions combined with OH ions to form a green precipitate, At the anode, the E value of OH is less positive that the
2+
0
–
iron(II) hydroxide. E value of Cl . Oxidation of water to O gas occurs more
0
–
2
Fe (aq) + 2OH (aq) → Fe(OH) (s) readily.
−
2+
2
Further oxidation by oxygen, produced brown precipitate, Oxygen gas is colourless.
hydrated iron(III) oxide or rust. Solution X in Set II: Concentrated hydrochloric acid
oxidation
Fe(OH )(s) ⎯⎯⎯→ Fe O .xH O(s) At the anode, the concentration of Cl ion is higher than
−
2 2 3 2
–
−
(b) (i) Metal X: Magnesium OH ion. Oxidation of Cl to Cl gas occurs more readily.
2
Metal Y: Lead Chlorine gas is yellow-green.
−
+
Magnesium is more electropositive than iron. (ii) H ions and Cl ions
Magnesium is more likely to release electrons compared (iii) Set I: Anode: 4OH (aq) → O (g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e −
−
2
to iron and oxidised. Cathode: 2H (aq) + 2e → H (g)
−
+
2+
Mg(s) → Mg (aq) + 2e − 2
Set II: Anode: 2Cl (aq) → Cl (g) + 2e −
−
2
Magnesium preventing iron from rusting. While lead is Cathode: 2H (aq) + 2e → H (g)
−
+
2
less electropositive than iron. Iron releases electrons and
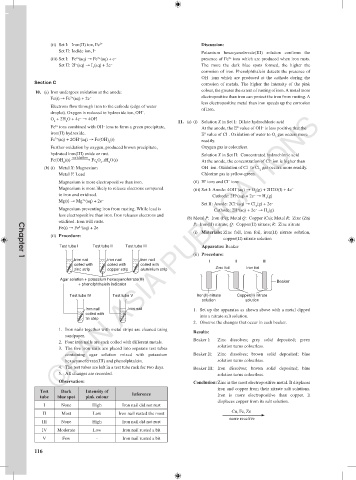
(b) Metal P: Iron (Fe); Metal Q: Copper (Cu); Metal R: Zinc (Zn)
oxidised. Iron will rusts. P: Iron(II) nitrate; Q: Copper(II) nitrate; R: Zinc nitrate
2+
Fe(s) → Fe (aq) + 2e −
(i) Materials: Zinc foil, iron foil, iron(II) nitrate solution,
(ii) Procedure:
copper(II) nitrate solution
Test tube I Test tube II Test tube III Apparatus: Beaker
(ii) Procedure:
Iron nail Iron nail Iron nail
I II III
Chapter 1
coiled with coiled with coiled with
zinc strip copper strip aluminium strip Zinc foil Iron foil
Agar solution + potassium hexacyanoferrate(III)
Beaker
+ phenolphthalein indicator
Test tube IV Test tube V Iron(II) nitrate Copper(II) nitrate
solution solution
Iron nail Iron nail 1. Set up the apparatus as shown above with a metal dipped
coiled with into a nitrate salt solution.
tin strip
2. Observe the changes that occur in each beaker.
1. Iron nails together with metal strips are cleaned using
Results:
sandpaper.
Beaker I: Zinc dissolves; grey solid deposited; green
2. Four iron nails are each coiled with different metals.
solution turns colourless.
3. The five iron nails are placed into separate test tubes
containing agar solution mixed with potassium Beaker II: Zinc dissolves; brown solid deposited; blue
hexacyanoferrate(III) and phenolphtalein. solution turns colourless.
4. The test tubes are left in a test tube rack for two days. Beaker III: Iron dissolves; brown solid deposited; blue
5. All changes are recorded. solution turns colourless.
Observation: Conclusion: Zinc is the most electropositive metal. It displaces
iron and copper from their nitrate salt solutions.
Test Dark Intensity of Inference
tube blue spot pink colour Iron is more electropositive than copper. It
displaces copper from its salt solution.
I None High Iron nail did not rust
Cu, Fe, Zn
II Most Low Iron nail rusted the most
more reactive
III None High Iron nail did not rust
IV Moderate Low Iron nail rusted a bit
V Few - Iron nail rusted a bit
116