Page 5 - 1202 Question Bank Mathematics Form 4
P. 5
Quadratic Functions and
Chapter 1 Equations in One Variable
NOTes
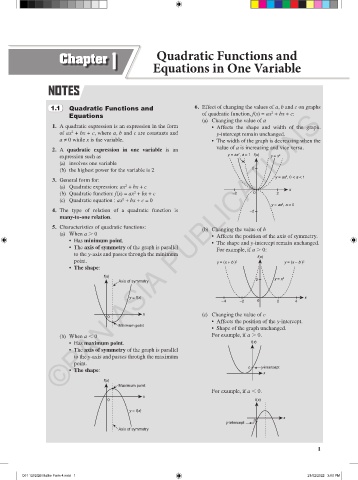
1.1 Quadratic Functions and 6. Effect of changing the values of a, b and c on graphs
Equations of quadratic function, f(x) = ax + bx + c:
2
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
(a) Changing the value of a
1. A quadratic expression is an expression in the form • Affects the shape and width of the graph.
of ax + bx + c, where a, b and c are constants and y-intercept remain unchanged.
2
a ≠ 0 while x is the variable. • The width of the graph is decreasing when the
2. A quadratic expression in one variable is an value of a is increasing and vice versa.
2
expression such as y = ax , a > 1 f(x) y = x 2
(a) involves one variable
(b) the highest power for the variable is 2 2
2
y = ax , 0 < a < 1
3. General form for:
2
(a) Quadratic expression: ax + bx + c
x
2
(b) Quadratic function: f(x) = ax + bx + c –2 0 2
2
(c) Quadratic equation : ax + bx + c = 0
y = ax , a < 0
2
4. The type of relation of a quadratic function is –2
many-to-one relation.
5. Characteristics of quadratic functions:
(b) Changing the value of b
(a) When a . 0
• Affects the position of the axis of symmetry.
• Has minimum point.
• The shape and y-intercept remain unchanged.
• The axis of symmetry of the graph is parallel
For example, if a . 0:
to the y-axis and passes through the minimum
f(x)
point. y = (x + b ) 2 y = (x – b ) 2
• The shape:
f(x) y = x 2
Axis of symmetry 2
y = f(x) x
–4 –2 0 2 4
x (c) Changing the value of c
0
• Affects the position of the y-intercept.
Minimum point
• Shape of the graph unchanged.
(b) When a , 0 For example, if a . 0.
• Has maximum point. f(x)
• The axis of symmetry of the graph is parallel
to the y-axis and passes through the maximum
point.
c y-intercept
• The shape:
x
f(x)
Maximum point
For example, if a , 0.
x
0 f(x)
y = f(x)
x
0
y-intercept c
Axis of symmetry
1
C01 1202QB Maths Form 4.indd 1 21/02/2022 3:00 PM