Page 345 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 345
Joe Smith 25
Sally Jones 28
Bob Johnson 37
Maria Doe 26
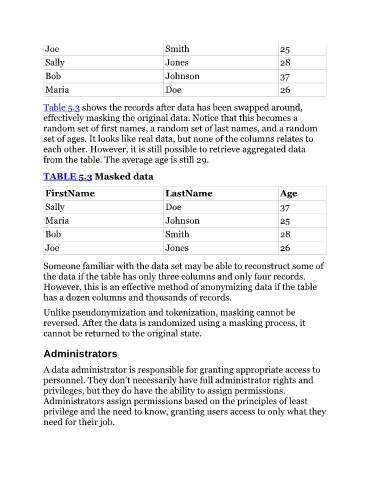
Table 5.3 shows the records after data has been swapped around,
effectively masking the original data. Notice that this becomes a
random set of first names, a random set of last names, and a random
set of ages. It looks like real data, but none of the columns relates to
each other. However, it is still possible to retrieve aggregated data
from the table. The average age is still 29.
TABLE 5.3 Masked data
FirstName LastName Age
Sally Doe 37
Maria Johnson 25
Bob Smith 28
Joe Jones 26
Someone familiar with the data set may be able to reconstruct some of
the data if the table has only three columns and only four records.
However, this is an effective method of anonymizing data if the table
has a dozen columns and thousands of records.
Unlike pseudonymization and tokenization, masking cannot be
reversed. After the data is randomized using a masking process, it
cannot be returned to the original state.
Administrators
A data administrator is responsible for granting appropriate access to
personnel. They don’t necessarily have full administrator rights and
privileges, but they do have the ability to assign permissions.
Administrators assign permissions based on the principles of least
privilege and the need to know, granting users access to only what they
need for their job.