Page 10 - Science Class 6 Times Publication
P. 10
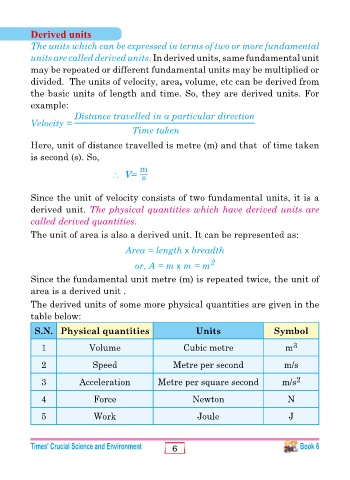
Derived units
The units which can be expressed in terms of two or more fundamental
units are called derived units. In derived units, same fundamental unit
may be repeated or different fundamental units may be multiplied or
divided. The units of velocity, area, volume, etc can be derived from
the basic units of length and time. So, they are derived units. For
example:
Distance travelled in a particular direction
Velocity =
Time taken
Here, unit of distance travelled is metre (m) and that of time taken
is second (s). So,
m
∴ V= s
Since the unit of velocity consists of two fundamental units, it is a
derived unit. The physical quantities which have derived units are
called derived quantities.
The unit of area is also a derived unit. It can be represented as:
Area = length x breadth
or, A = m x m = m 2
Since the fundamental unit metre (m) is repeated twice, the unit of
area is a derived unit .
The derived units of some more physical quantities are given in the
table below:
S.N. Physical quantities Units Symbol
1 Volume Cubic metre m 3
2 Speed Metre per second m/s
3 Acceleration Metre per square second m/s 2
4 Force Newton N
5 Work Joule J
Times' Crucial Science and Environment 6 Book 6