Page 76 - Math Smart - 7
P. 76
Help
Sheet
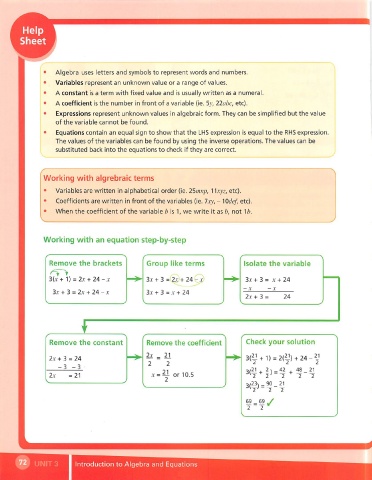
Algebra uses letters and symbols to represent words and numbers.
Variables represent an unknown value or a range of values.
A constant is a term with fixed value and is usually written as a numeral.
A coefficient is the number in front of a variable (ie. 5y, 22abc, etc).
Expressions represent unknown values in algebraic form. They can be simplified but the value
of the variable cannot be found.
Equations contain an equal sign to show that the LHS expression is equal to the RHS expression.
The values of the variables can be found by using the inverse operations. The values can be
substituted back into the equations to check if they are correct.
Working with algrebraic terms
• Variables are written in alphabetical order (ie. 25mnp, 1 ^xyz, etc).
• Coefficients are written in front of the variables (ie. 7xy, - ^OcJef, etc).
• When the coefficient of the variable b is 1, we write it as b, not ^b.
Working with an equation step-by-step
Remove the brackets Group like terms Isolate the variable
3{x + \) = 2x + 2A-X 3x + 3=(2x}+ 24 Q) 3x + 3 = X + 24
- X -
X
3x + 3 = 2x +24-X 3x + 3 = X + 24
2x + 3 = 24
f
Remove the constant Remove the coefficient Check your solution
2x ^ 21 21
2x + 3 = 24 3(^ + 1) = 2(^) + 24- 2
2 2
-3 -3
x = ^ or 10.5 3(£i+ |) = « +
2x = 21 2 2' 2
2
^2^" 2 2
2 2
UNITS Introduction to Algebra and Equations