Page 229 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 229
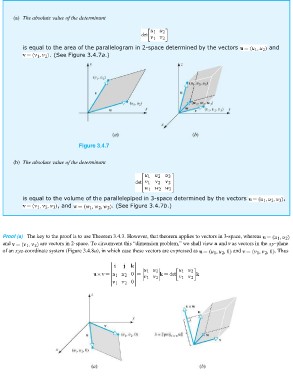
(a) The absolute value of the determinant and
is equal to the area of the parallelogram in 2-space determined by the vectors
. (See Figure 3.4.7a.)
Figure 3.4.7
(b) The absolute value of the determinant
is equal to the volume of the parallelepiped in 3-space determined by the vectors ,
, and . (See Figure 3.4.7b.)
Proof (a) The key to the proof is to use Theorem 3.4.3. However, that theorem applies to vectors in 3-space, whereas
and are vectors in 2-space. To circumvent this “dimension problem,” we shall view u and v as vectors in the -plane
. Thus
of an -coordinate system (Figure 3.4.8a), in which case these vectors are expressed as and