Page 304 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 304
4.3 In this section we shall investigate the relationship between the invertibility of a
matrix and properties of the corresponding matrix transformation. We shall also
PROPERTIES OF LINEAR obtain a characterization of linear transformations from to that will form
TRANSFORMATIONS the basis for more general linear transformations to be discussed in subsequent
FROM TO sections, and we shall discuss some geometric properties of eigenvectors.
One-to-One Linear Transformations
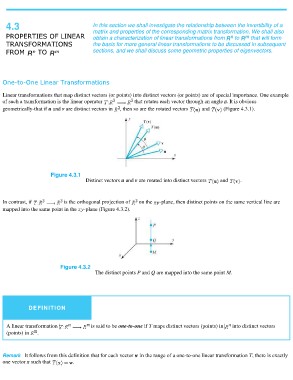
Linear transformations that map distinct vectors (or points) into distinct vectors (or points) are of special importance. One example
of such a transformation is the linear operator that rotates each vector through an angle . It is obvious
geometrically-that if u and v are distinct vectors in , then so are the rotated vectors and (Figure 4.3.1).
Figure 4.3.1 and .
Distinct vectors u and v are rotated into distinct vectors
In contrast, if is the orthogonal projection of on the -plane, then distinct points on the same vertical line are
mapped into the same point in the -plane (Figure 4.3.2).
Figure 4.3.2
The distinct points P and Q are mapped into the same point M.
DEFINITION is said to be one-to-one if T maps distinct vectors (points) in into distinct vectors
A linear transformation
(points) in .
Remark It follows from this definition that for each vector w in the range of a one-to-one linear transformation T, there is exactly
one vector x such that .